Self-trained Deep Ordinal Regression for End-to-End Video Anomaly Detection
Paper and Code
Mar 15, 2020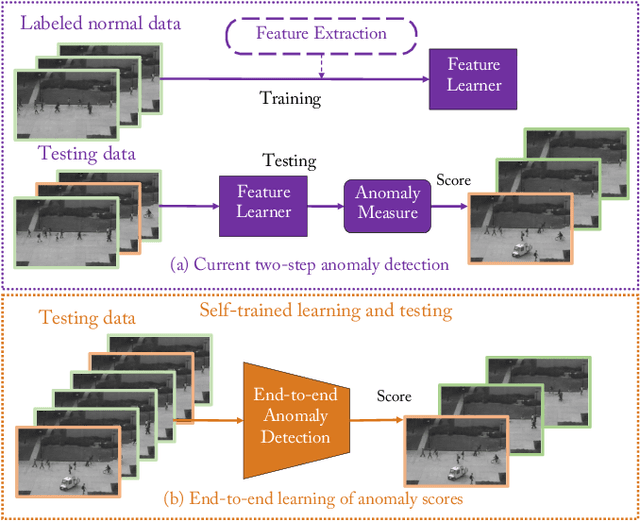
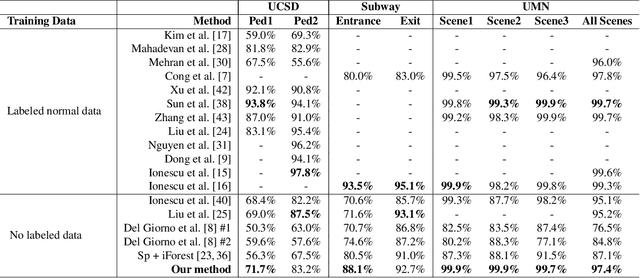
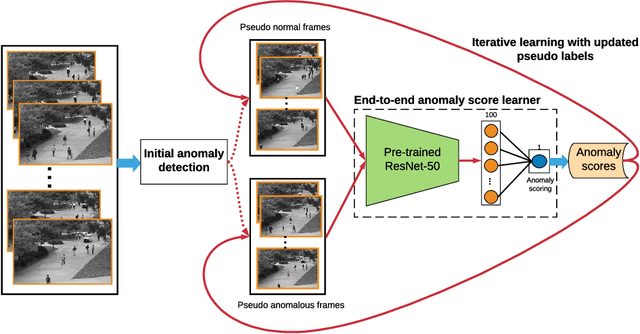
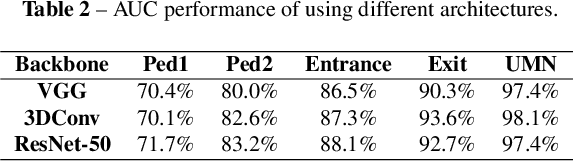
Video anomaly detection is of critical practical importance to a variety of real applications because it allows human attention to be focused on events that are likely to be of interest, in spite of an otherwise overwhelming volume of video. We show that applying self-trained deep ordinal regression to video anomaly detection overcomes two key limitations of existing methods, namely, 1) being highly dependent on manually labeled normal training data; and 2) sub-optimal feature learning. By formulating a surrogate two-class ordinal regression task we devise an end-to-end trainable video anomaly detection approach that enables joint representation learning and anomaly scoring without manually labeled normal/abnormal data. Experiments on eight real-world video scenes show that our proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art methods that require no labeled training data by a substantial margin, and enables easy and accurate localization of the identified anomalies. Furthermore, we demonstrate that our method offers effective human-in-the-loop anomaly detection which can be critical in applications where anomalies are rare and the false-negative cost is high.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge