Self-supervised learning for audio-visual speaker diarization
Paper and Code
Feb 13, 2020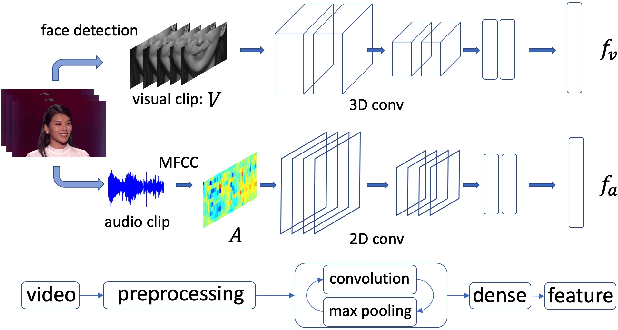

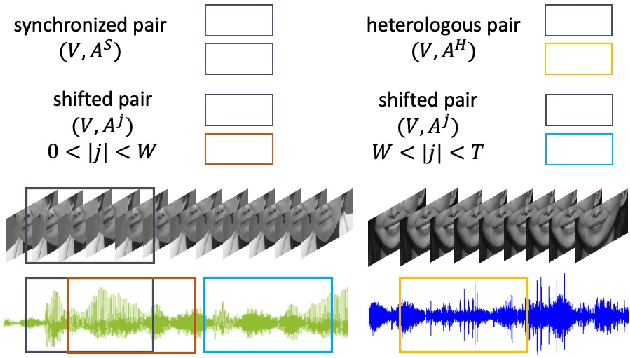
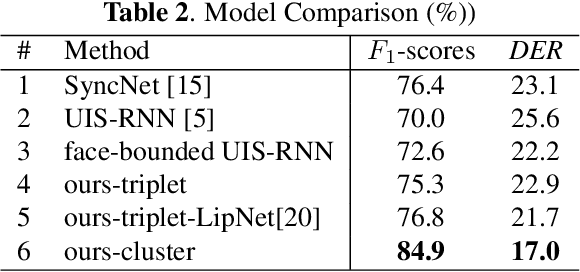
Speaker diarization, which is to find the speech segments of specific speakers, has been widely used in human-centered applications such as video conferences or human-computer interaction systems. In this paper, we propose a self-supervised audio-video synchronization learning method to address the problem of speaker diarization without massive labeling effort. We improve the previous approaches by introducing two new loss functions: the dynamic triplet loss and the multinomial loss. We test them on a real-world human-computer interaction system and the results show our best model yields a remarkable gain of +8%F1-scoresas well as diarization error rate reduction. Finally, we introduce a new large scale audio-video corpus designed to fill the vacancy of audio-video datasets in Chinese.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge