Self-paced learning to improve text row detection in historical documents with missing labels
Paper and Code
Feb 02, 2022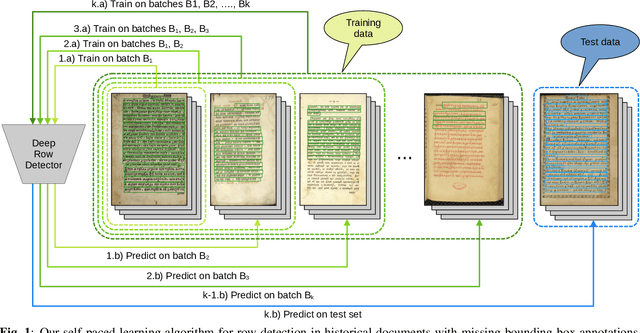
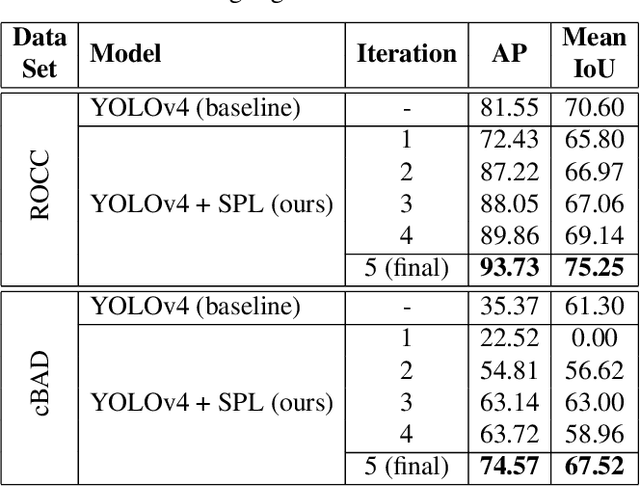

An important preliminary step of optical character recognition systems is the detection of text rows. To address this task in the context of historical data with missing labels, we propose a self-paced learning algorithm capable of improving the row detection performance. We conjecture that pages with more ground-truth bounding boxes are less likely to have missing annotations. Based on this hypothesis, we sort the training examples in descending order with respect to the number of ground-truth bounding boxes, and organize them into k batches. Using our self-paced learning method, we train a row detector over k iterations, progressively adding batches with less ground-truth annotations. At each iteration, we combine the ground-truth bounding boxes with pseudo-bounding boxes (bounding boxes predicted by the model itself) using non-maximum suppression, and we include the resulting annotations at the next training iteration. We demonstrate that our self-paced learning strategy brings significant performance gains on two data sets of historical documents, improving the average precision of YOLOv4 with more than 12% on one data set and 39% on the other.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge