Self-Discriminative Modeling for Anomalous Graph Detection
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2023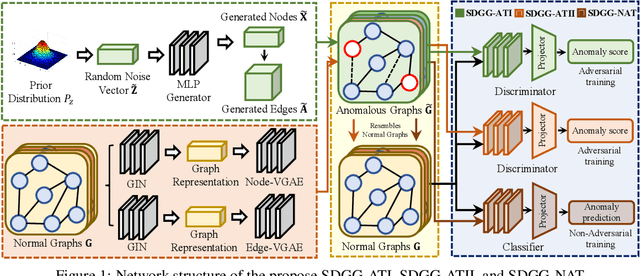
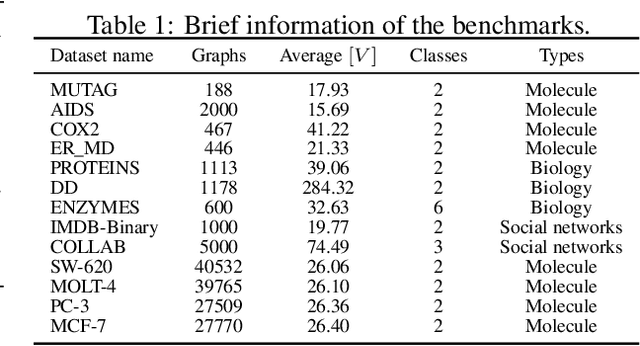
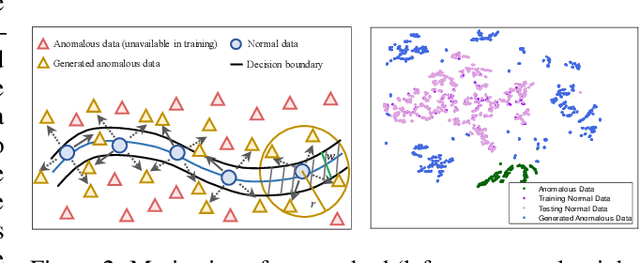
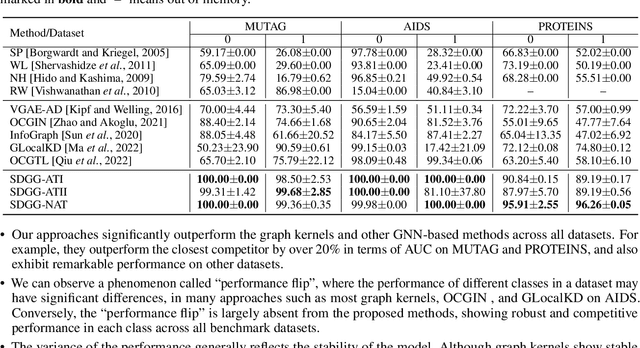
This paper studies the problem of detecting anomalous graphs using a machine learning model trained on only normal graphs, which has many applications in molecule, biology, and social network data analysis. We present a self-discriminative modeling framework for anomalous graph detection. The key idea, mathematically and numerically illustrated, is to learn a discriminator (classifier) from the given normal graphs together with pseudo-anomalous graphs generated by a model jointly trained, where we never use any true anomalous graphs and we hope that the generated pseudo-anomalous graphs interpolate between normal ones and (real) anomalous ones. Under the framework, we provide three algorithms with different computational efficiencies and stabilities for anomalous graph detection. The three algorithms are compared with several state-of-the-art graph-level anomaly detection baselines on nine popular graph datasets (four with small size and five with moderate size) and show significant improvement in terms of AUC. The success of our algorithms stems from the integration of the discriminative classifier and the well-posed pseudo-anomalous graphs, which provide new insights for anomaly detection. Moreover, we investigate our algorithms for large-scale imbalanced graph datasets. Surprisingly, our algorithms, though fully unsupervised, are able to significantly outperform supervised learning algorithms of anomalous graph detection. The corresponding reason is also analyzed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge