Seeing Is Believing: Black-Box Membership Inference Attacks Against Retrieval Augmented Generation
Paper and Code
Jun 27, 2024
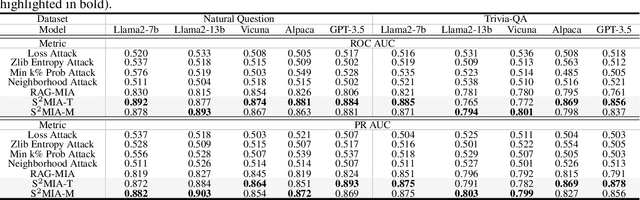
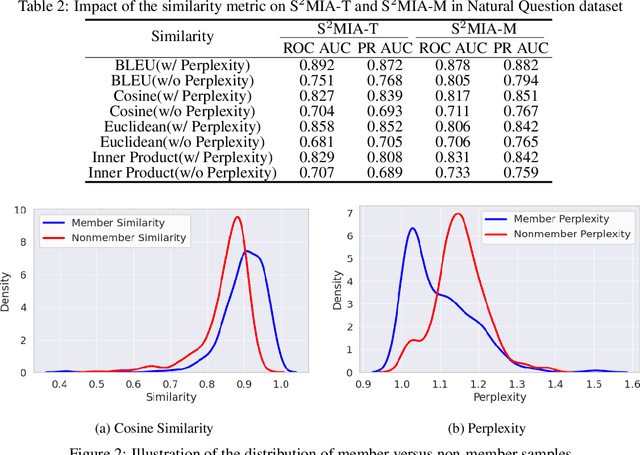
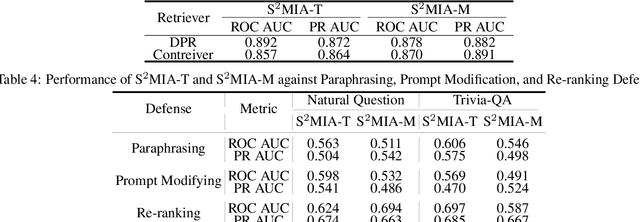
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a state-of-the-art technique that enhances Large Language Models (LLMs) by retrieving relevant knowledge from an external, non-parametric database. This approach aims to mitigate common LLM issues such as hallucinations and outdated knowledge. Although existing research has demonstrated security and privacy vulnerabilities within RAG systems, making them susceptible to attacks like jailbreaks and prompt injections, the security of the RAG system's external databases remains largely underexplored. In this paper, we employ Membership Inference Attacks (MIA) to determine whether a sample is part of the knowledge database of a RAG system, using only black-box API access. Our core hypothesis posits that if a sample is a member, it will exhibit significant similarity to the text generated by the RAG system. To test this, we compute the cosine similarity and the model's perplexity to establish a membership score, thereby building robust features. We then introduce two novel attack strategies: a Threshold-based Attack and a Machine Learning-based Attack, designed to accurately identify membership. Experimental validation of our methods has achieved a ROC AUC of 82%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge