Searching to Learn with Instructional Scaffolding
Paper and Code
Nov 29, 2021
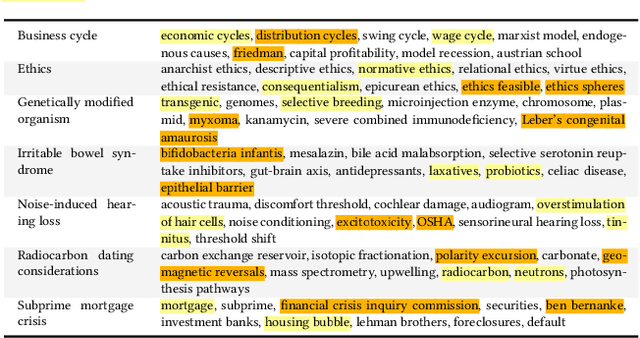
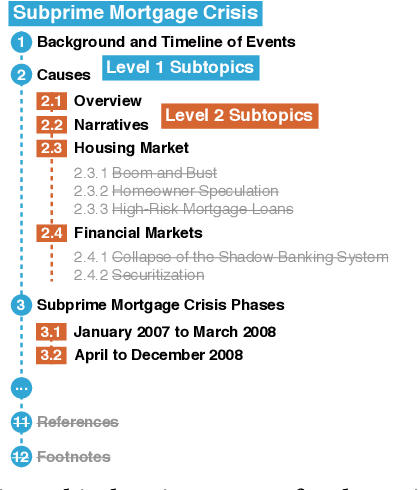
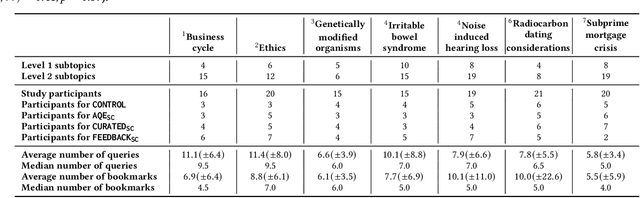
Search engines are considered the primary tool to assist and empower learners in finding information relevant to their learning goals-be it learning something new, improving their existing skills, or just fulfilling a curiosity. While several approaches for improving search engines for the learning scenario have been proposed, instructional scaffolding has not been studied in the context of search as learning, despite being shown to be effective for improving learning in both digital and traditional learning contexts. When scaffolding is employed, instructors provide learners with support throughout their autonomous learning process. We hypothesize that the usage of scaffolding techniques within a search system can be an effective way to help learners achieve their learning objectives whilst searching. As such, this paper investigates the incorporation of scaffolding into a search system employing three different strategies (as well as a control condition): (I) AQE_{SC}, the automatic expansion of user queries with relevant subtopics; (ii) CURATED_{SC}, the presenting of a manually curated static list of relevant subtopics on the search engine result page; and (iii) FEEDBACK_{SC}, which projects real-time feedback about a user's exploration of the topic space on top of the CURATED_{SC} visualization. To investigate the effectiveness of these approaches with respect to human learning, we conduct a user study (N=126) where participants were tasked with searching and learning about topics such as `genetically modified organisms'. We find that (I) the introduction of the proposed scaffolding methods does not significantly improve learning gains. However, (ii) it does significantly impact search behavior. Furthermore, (iii) immediate feedback of the participants' learning leads to undesirable user behavior, with participants focusing on the feedback gauges instead of learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge