Scrutinizing Shipment Records To Thwart Illegal Timber Trade
Paper and Code
Jul 31, 2022
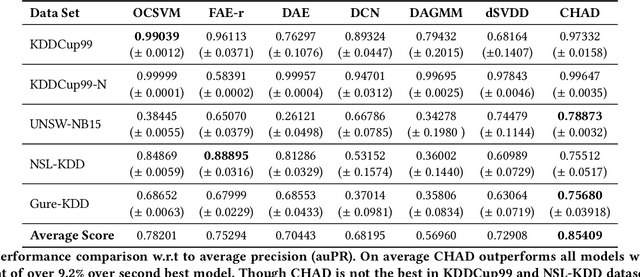
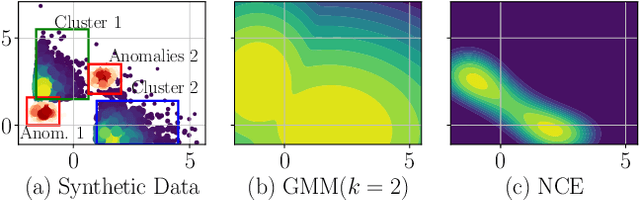
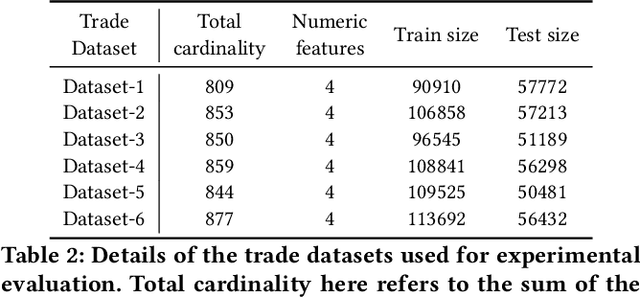
Timber and forest products made from wood, like furniture, are valuable commodities, and like the global trade of many highly-valued natural resources, face challenges of corruption, fraud, and illegal harvesting. These grey and black market activities in the wood and forest products sector are not limited to the countries where the wood was harvested, but extend throughout the global supply chain and have been tied to illicit financial flows, like trade-based money laundering, document fraud, species mislabeling, and other illegal activities. The task of finding such fraudulent activities using trade data, in the absence of ground truth, can be modelled as an unsupervised anomaly detection problem. However existing approaches suffer from certain shortcomings in their applicability towards large scale trade data. Trade data is heterogeneous, with both categorical and numerical attributes in a tabular format. The overall challenge lies in the complexity, volume and velocity of data, with large number of entities and lack of ground truth labels. To mitigate these, we propose a novel unsupervised anomaly detection -- Contrastive Learning based Heterogeneous Anomaly Detection (CHAD) that is generally applicable for large-scale heterogeneous tabular data. We demonstrate our model CHAD performs favorably against multiple comparable baselines for public benchmark datasets, and outperforms them in the case of trade data. More importantly we demonstrate our approach reduces assumptions and efforts required hyperparameter tuning, which is a key challenging aspect in an unsupervised training paradigm. Specifically, our overarching objective pertains to detecting suspicious timber shipments and patterns using Bill of Lading trade record data. Detecting anomalous transactions in shipment records can enable further investigation by government agencies and supply chain constituents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge