Screening Rules and its Complexity for Active Set Identification
Paper and Code
Sep 06, 2020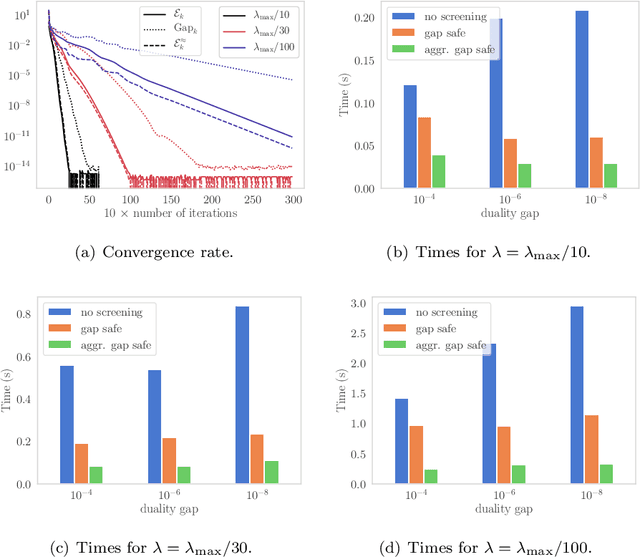
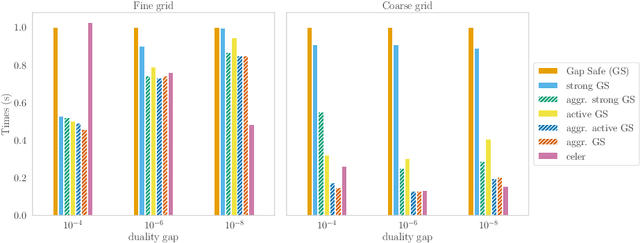
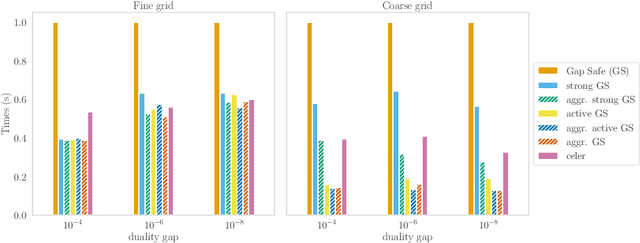

Screening rules were recently introduced as a technique for explicitly identifying active structures such as sparsity, in optimization problem arising in machine learning. This has led to new methods of acceleration based on a substantial dimension reduction. We show that screening rules stem from a combination of natural properties of subdifferential sets and optimality conditions, and can hence be understood in a unified way. Under mild assumptions, we analyze the number of iterations needed to identify the optimal active set for any converging algorithm. We show that it only depends on its convergence rate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge