Robustness and Confounders in the Demographic Alignment of LLMs with Human Perceptions of Offensiveness
Paper and Code
Nov 13, 2024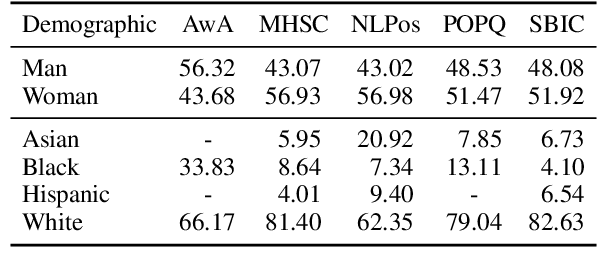
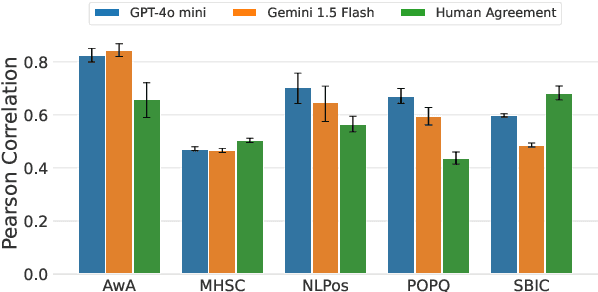
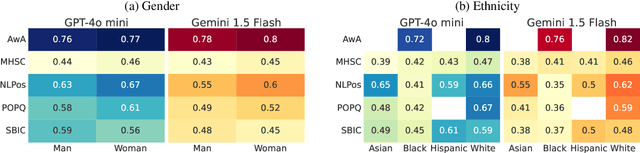
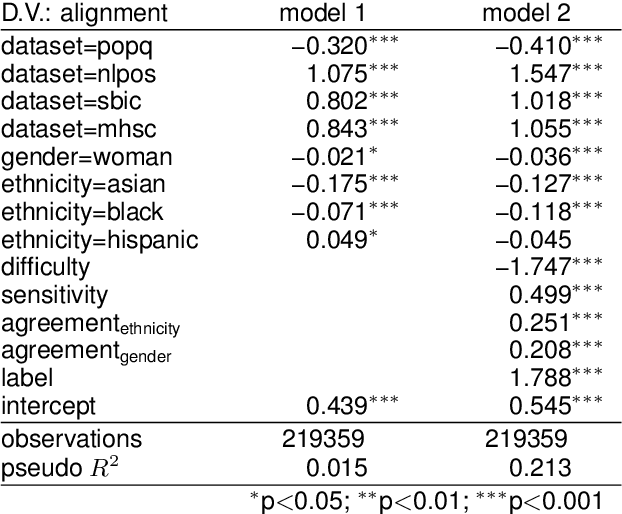
Large language models (LLMs) are known to exhibit demographic biases, yet few studies systematically evaluate these biases across multiple datasets or account for confounding factors. In this work, we examine LLM alignment with human annotations in five offensive language datasets, comprising approximately 220K annotations. Our findings reveal that while demographic traits, particularly race, influence alignment, these effects are inconsistent across datasets and often entangled with other factors. Confounders -- such as document difficulty, annotator sensitivity, and within-group agreement -- account for more variation in alignment patterns than demographic traits alone. Specifically, alignment increases with higher annotator sensitivity and group agreement, while greater document difficulty corresponds to reduced alignment. Our results underscore the importance of multi-dataset analyses and confounder-aware methodologies in developing robust measures of demographic bias in LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge