Robustness Analysis of Face Obscuration
Paper and Code
May 13, 2019
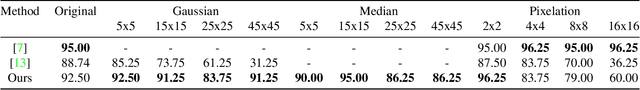
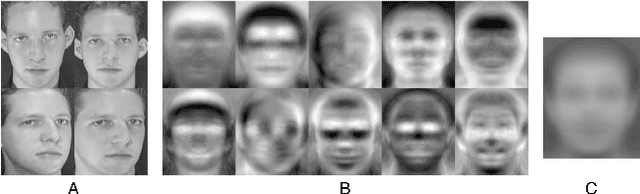
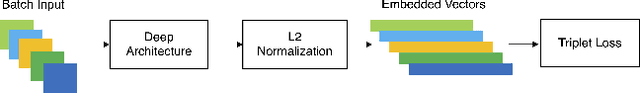
Face obscuration is often needed by law enforcement or mass media outlets to provide privacy protection. Sharing sensitive content where the obscuration or redaction technique may have failed to completely remove all identifiable traces can lead to life-threatening consequences. Hence, it is critical to be able to systematically measure the face obscuration performance of a given technique. In this paper we propose to measure the effectiveness of three obscuration techniques: Gaussian blurring, median blurring, and pixelation. We do so by identifying the redacted faces under two scenarios: classifying an obscured face into a group of identities and comparing the similarity of an obscured face with a clear face. Threat modeling is also considered to provide a vulnerability analysis for each studied obscuration technique. Based on our evaluation, we show that pixelation-based face obscuration approaches are the most effective.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge