Robust SLAM Systems: Are We There Yet?
Paper and Code
Sep 27, 2021
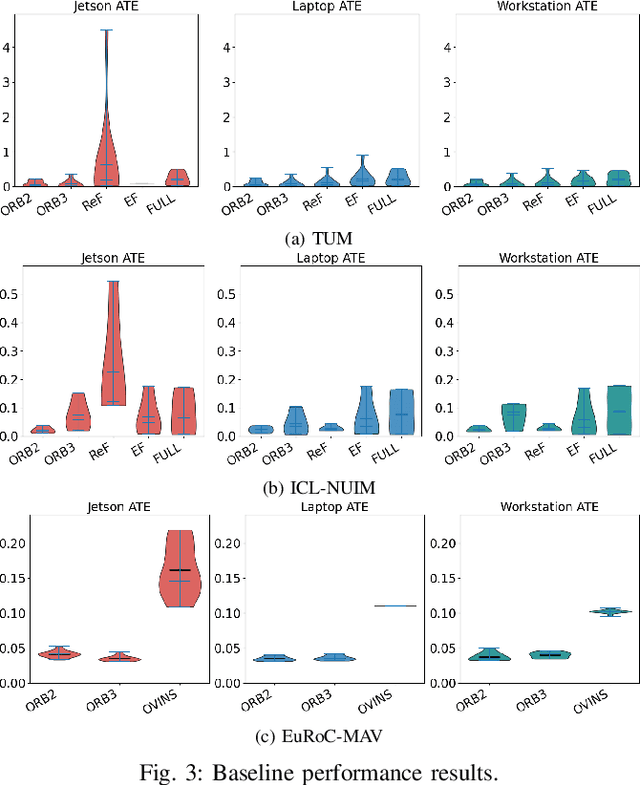
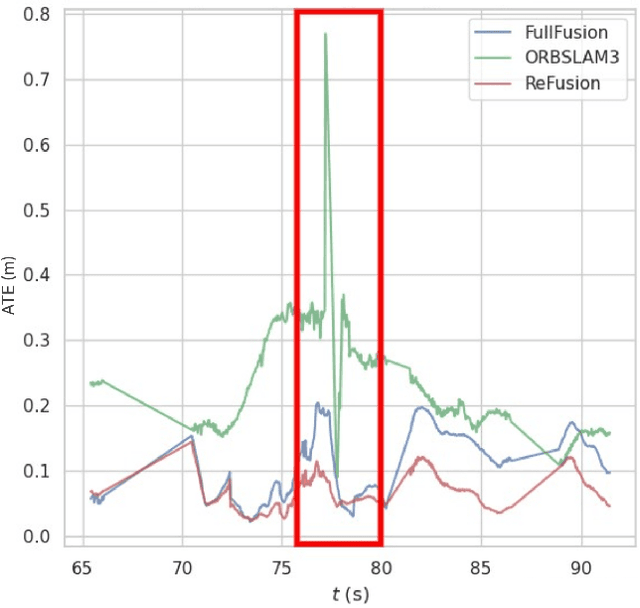
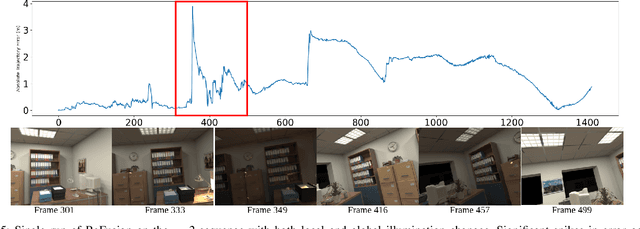
Progress in the last decade has brought about significant improvements in the accuracy and speed of SLAM systems, broadening their mapping capabilities. Despite these advancements, long-term operation remains a major challenge, primarily due to the wide spectrum of perturbations robotic systems may encounter. Increasing the robustness of SLAM algorithms is an ongoing effort, however it usually addresses a specific perturbation. Generalisation of robustness across a large variety of challenging scenarios is not well-studied nor understood. This paper presents a systematic evaluation of the robustness of open-source state-of-the-art SLAM algorithms with respect to challenging conditions such as fast motion, non-uniform illumination, and dynamic scenes. The experiments are performed with perturbations present both independently of each other, as well as in combination in long-term deployment settings in unconstrained environments (lifelong operation).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge