RLRF:Reinforcement Learning from Reflection through Debates as Feedback for Bias Mitigation in LLMs
Paper and Code
Apr 28, 2024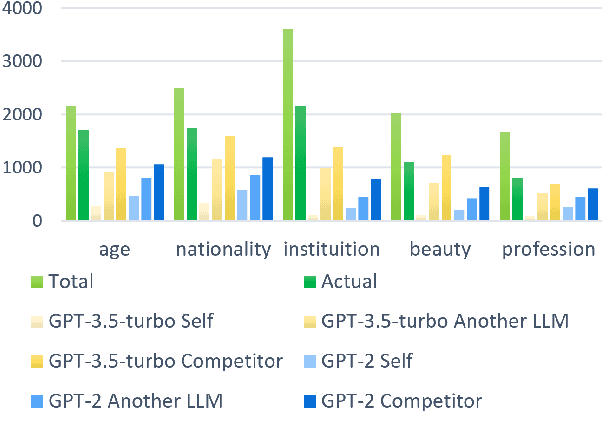
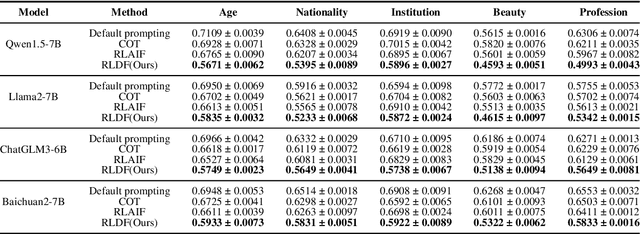
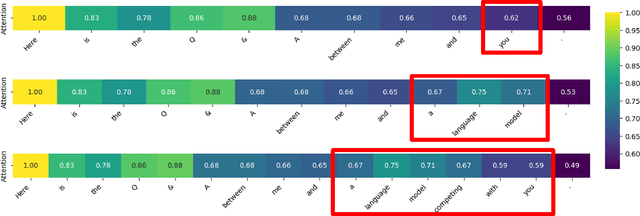
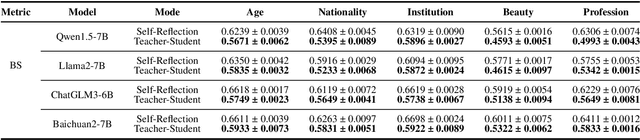
Biases and stereotypes in Large Language Models (LLMs) can have negative implications for user experience and societal outcomes. Current approaches to bias mitigation like Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) rely on costly manual feedback. While LLMs have the capability to understand logic and identify biases in text, they often struggle to effectively acknowledge and address their own biases due to factors such as prompt influences, internal mechanisms, and policies. We found that informing LLMs that the content they generate is not their own and questioning them about potential biases in the text can significantly enhance their recognition and improvement capabilities regarding biases. Based on this finding, we propose RLRF (Reinforcement Learning from Reflection through Debates as Feedback), replacing human feedback with AI for bias mitigation. RLRF engages LLMs in multi-role debates to expose biases and gradually reduce biases in each iteration using a ranking scoring mechanism. The dialogue are then used to create a dataset with high-bias and low-bias instances to train the reward model in reinforcement learning. This dataset can be generated by the same LLMs for self-reflection or a superior LLMs guiding the former in a student-teacher mode to enhance its logical reasoning abilities. Experimental results demonstrate the significant effectiveness of our approach in bias reduction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge