Rethinking Portrait Matting with Privacy Preserving
Paper and Code
Mar 31, 2022
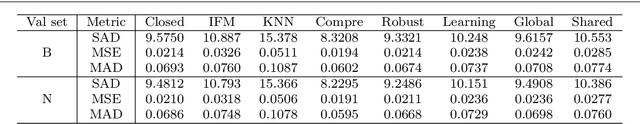

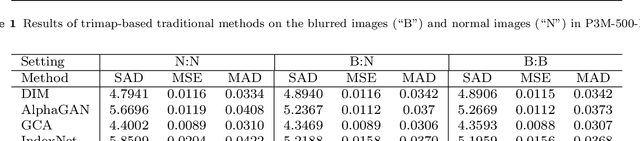
Recently, there has been an increasing concern about the privacy issue raised by using personally identifiable information in machine learning. However, previous portrait matting methods were all based on identifiable portrait images. To fill the gap, we present P3M-10k in this paper, which is the first large-scale anonymized benchmark for Privacy-Preserving Portrait Matting (P3M). P3M-10k consists of 10,000 high-resolution face-blurred portrait images along with high-quality alpha mattes. We systematically evaluate both trimap-free and trimap-based matting methods on P3M-10k and find that existing matting methods show different generalization abilities under the privacy preserving training setting, i.e., training only on face-blurred images while testing on arbitrary images. Based on the gained insights, we propose a unified matting model named P3M-Net consisting of three carefully designed integration modules that can perform privacy-insensitive semantic perception and detail-reserved matting simultaneously. We further design multiple variants of P3M-Net with different CNN and transformer backbones and identify the difference in their generalization abilities. To further mitigate this issue, we devise a simple yet effective Copy and Paste strategy (P3M-CP) that can borrow facial information from public celebrity images without privacy concerns and direct the network to reacquire the face context at both data and feature levels. P3M-CP only brings a few additional computations during training, while enabling the matting model to process both face-blurred and normal images without extra effort during inference. Extensive experiments on P3M-10k demonstrate the superiority of P3M-Net over state-of-the-art methods and the effectiveness of P3M-CP in improving the generalization ability of P3M-Net, implying a great significance of P3M for future research and real-world applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge