Resource Heterogeneity-Aware and Utilization-Enhanced Scheduling for Deep Learning Clusters
Paper and Code
Mar 13, 2025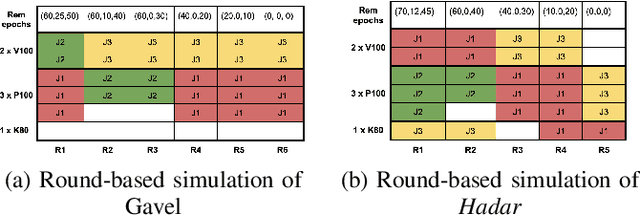
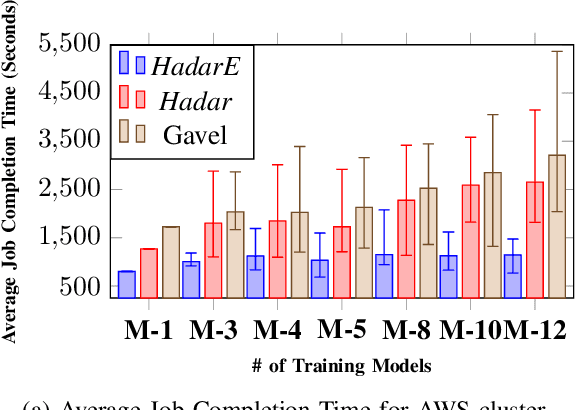
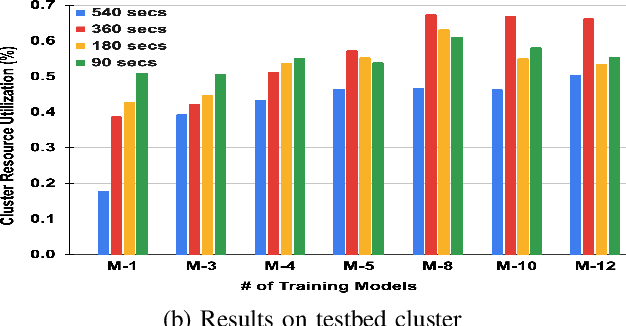
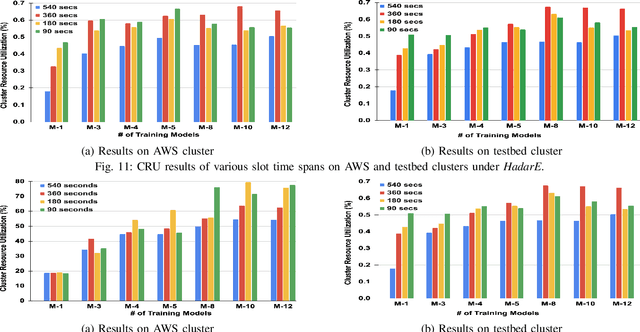
Scheduling deep learning (DL) models to train on powerful clusters with accelerators like GPUs and TPUs, presently falls short, either lacking fine-grained heterogeneity awareness or leaving resources substantially under-utilized. To fill this gap, we propose a novel design of a task-level heterogeneity-aware scheduler, {\em Hadar}, based on an optimization framework that can boost resource utilization. {\em Hadar} leverages the performance traits of DL jobs on a heterogeneous DL cluster, characterizes the task-level performance heterogeneity in the optimization problem, and makes scheduling decisions across both spatial and temporal dimensions. %with the objective to reduce the average job completion time of DL jobs. It involves the primal-dual framework employing a dual subroutine, to solve the optimization problem and guide the scheduling design. Our trace-driven simulation with representative DL model training workloads demonstrates that {\em Hadar} accelerates the total time duration by 1.20$\times$ when compared with its state-of-the-art heterogeneity-aware counterpart, Gavel. Further, our {\em Hadar} scheduler is enhanced to {\em HadarE} by forking each job into multiple copies to let a job train concurrently on heterogeneous GPUs resided on separate available nodes (i.e., machines or servers) for resource utilization enhancement. {\em HadarE} is evaluated extensively on physical DL clusters for comparison with {\em Hadar} and Gavel. With substantial enhancement in cluster resource utilization (by 1.45$\times$), {\em HadarE} exhibits considerable speed-ups in DL model training, reducing the total time duration by 50\% (or 80\%) on an Amazon's AWS (or our lab) cluster, while producing trained DL models with consistently better inference quality than those trained by \textit{Hadar}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge