Residual-based Language Models are Free Boosters for Biomedical Imaging
Paper and Code
Mar 28, 2024
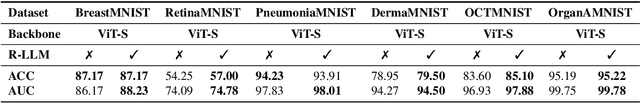

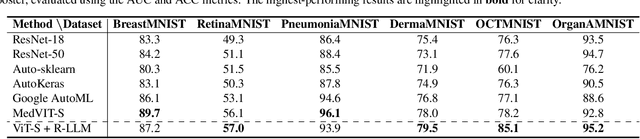
In this study, we uncover the unexpected efficacy of residual-based large language models (LLMs) as part of encoders for biomedical imaging tasks, a domain traditionally devoid of language or textual data. The approach diverges from established methodologies by utilizing a frozen transformer block, extracted from pre-trained LLMs, as an innovative encoder layer for the direct processing of visual tokens. This strategy represents a significant departure from the standard multi-modal vision-language frameworks, which typically hinge on language-driven prompts and inputs. We found that these LLMs could boost performance across a spectrum of biomedical imaging applications, including both 2D and 3D visual classification tasks, serving as plug-and-play boosters. More interestingly, as a byproduct, we found that the proposed framework achieved superior performance, setting new state-of-the-art results on extensive, standardized datasets in MedMNIST-2D and 3D. Through this work, we aim to open new avenues for employing LLMs in biomedical imaging and enriching the understanding of their potential in this specialized domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge