Research on Feature Extraction Data Processing System For MRI of Brain Diseases Based on Computer Deep Learning
Paper and Code
Jun 23, 2024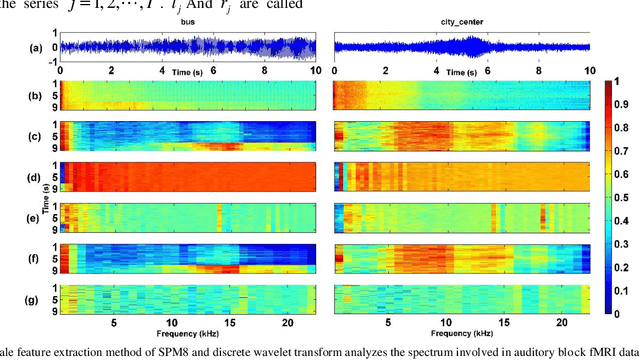
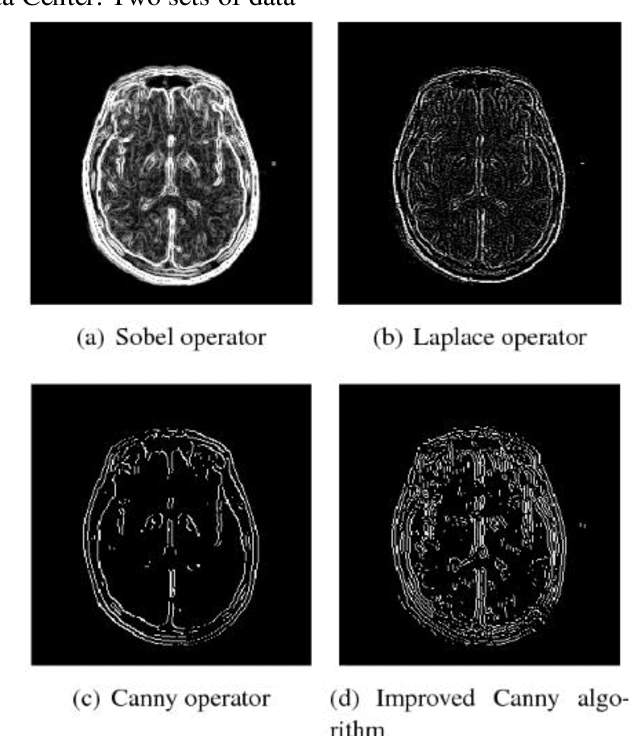

Most of the existing wavelet image processing techniques are carried out in the form of single-scale reconstruction and multiple iterations. However, processing high-quality fMRI data presents problems such as mixed noise and excessive computation time. This project proposes the use of matrix operations by combining mixed noise elimination methods with wavelet analysis to replace traditional iterative algorithms. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) of the auditory cortex of a single subject is analyzed and compared to the wavelet domain signal processing technology based on repeated times and the world's most influential SPM8. Experiments show that this algorithm is the fastest in computing time, and its detection effect is comparable to the traditional iterative algorithm. However, this has a higher practical value for the processing of FMRI data. In addition, the wavelet analysis method proposed signal processing to speed up the calculation rate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge