Reproduction and Replication of an Adversarial Stylometry Experiment
Paper and Code
Aug 15, 2022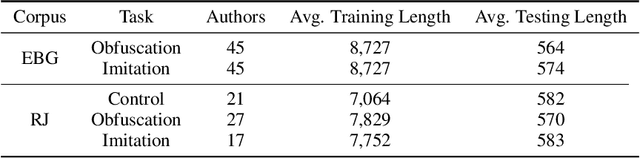
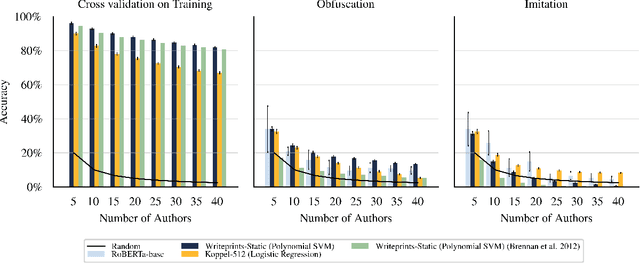
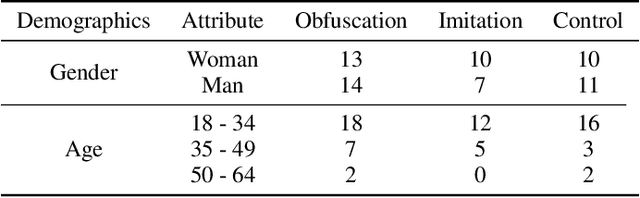
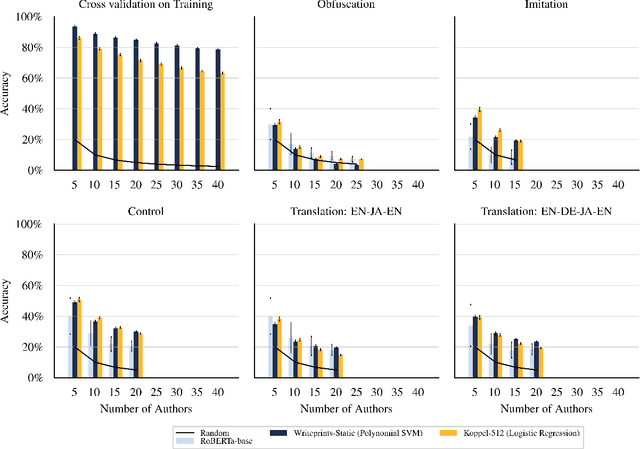
Maintaining anonymity while communicating using natural language remains a challenge. Standard authorship attribution techniques that analyze candidate authors' writing styles achieve uncomfortably high accuracy even when the number of candidate authors is high. Adversarial stylometry defends against authorship attribution with the goal of preventing unwanted deanonymization. This paper reproduces and replicates experiments in a seminal study of defenses against authorship attribution (Brennan et al., 2012). We are able to successfully reproduce and replicate the original results, although we conclude that the effectiveness of the defenses studied is overstated due to a lack of a control group in the original study. In our replication, we find new evidence suggesting that an entirely automatic method, round-trip translation, merits re-examination as it appears to reduce the effectiveness of established authorship attribution methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge