Representation Matters: Assessing the Importance of Subgroup Allocations in Training Data
Paper and Code
Mar 05, 2021
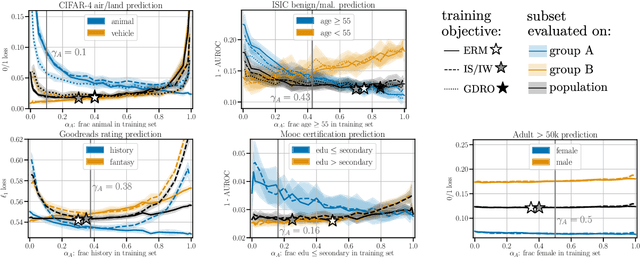
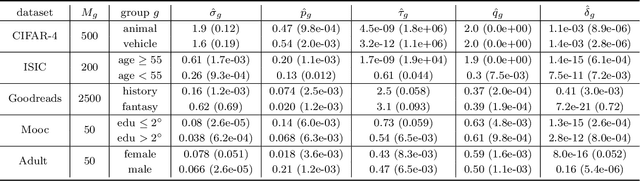
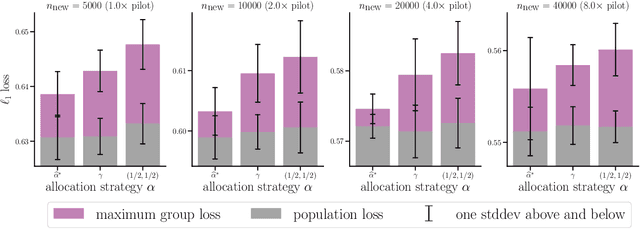
Collecting more diverse and representative training data is often touted as a remedy for the disparate performance of machine learning predictors across subpopulations. However, a precise framework for understanding how dataset properties like diversity affect learning outcomes is largely lacking. By casting data collection as part of the learning process, we demonstrate that diverse representation in training data is key not only to increasing subgroup performances, but also to achieving population level objectives. Our analysis and experiments describe how dataset compositions influence performance and provide constructive results for using trends in existing data, alongside domain knowledge, to help guide intentional, objective-aware dataset design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge