Relaxed Contrastive Learning for Federated Learning
Paper and Code
Jan 10, 2024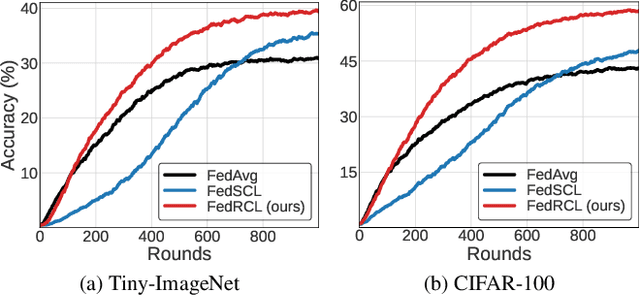
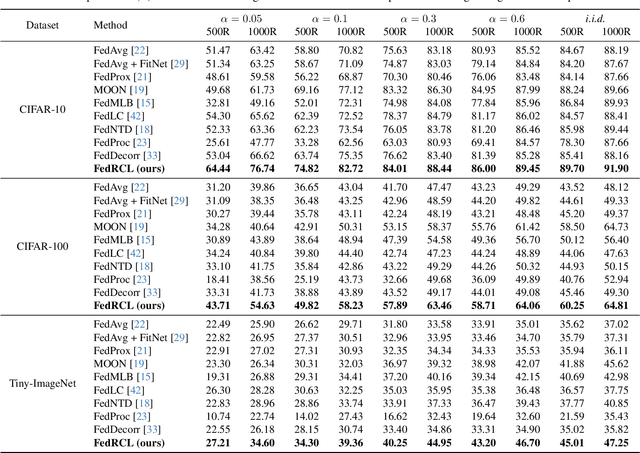
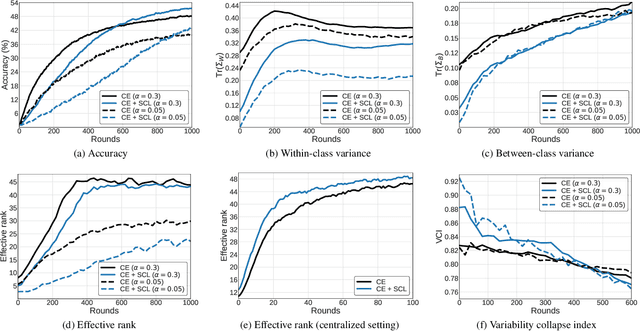
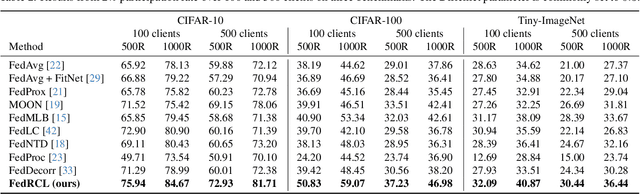
We propose a novel contrastive learning framework to effectively address the challenges of data heterogeneity in federated learning. We first analyze the inconsistency of gradient updates across clients during local training and establish its dependence on the distribution of feature representations, leading to the derivation of the supervised contrastive learning (SCL) objective to mitigate local deviations. In addition, we show that a na\"ive adoption of SCL in federated learning leads to representation collapse, resulting in slow convergence and limited performance gains. To address this issue, we introduce a relaxed contrastive learning loss that imposes a divergence penalty on excessively similar sample pairs within each class. This strategy prevents collapsed representations and enhances feature transferability, facilitating collaborative training and leading to significant performance improvements. Our framework outperforms all existing federated learning approaches by huge margins on the standard benchmarks through extensive experimental results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge