Reinforced Decoder: Towards Training Recurrent Neural Networks for Time Series Forecasting
Paper and Code
Jun 14, 2024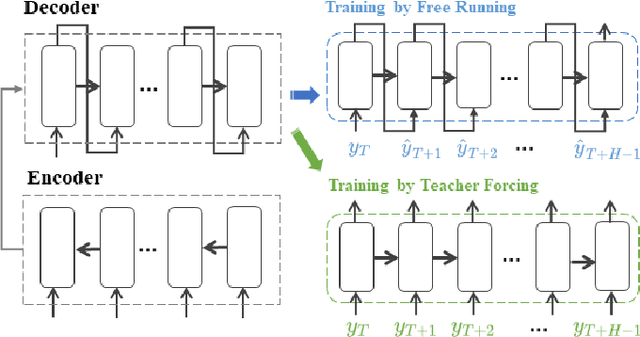
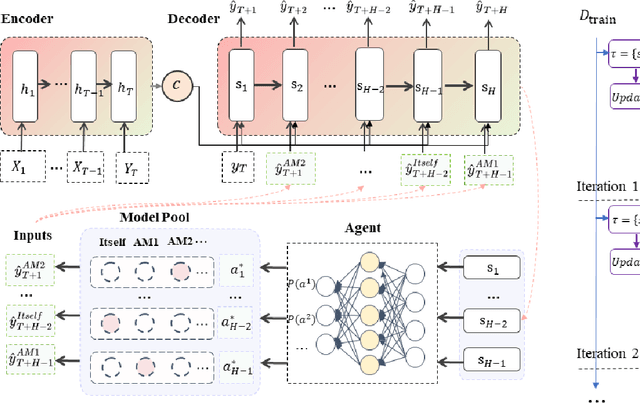
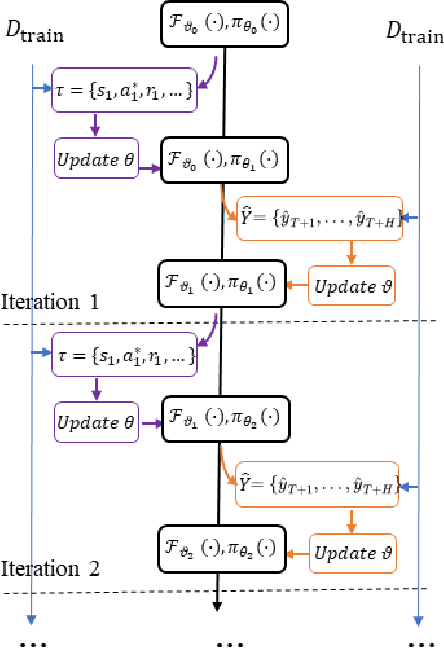
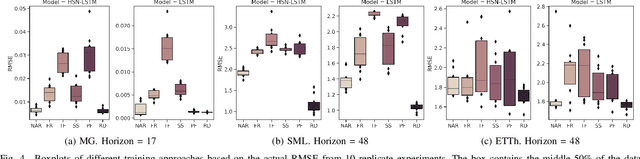
Recurrent neural network-based sequence-to-sequence models have been extensively applied for multi-step-ahead time series forecasting. These models typically involve a decoder trained using either its previous forecasts or the actual observed values as the decoder inputs. However, relying on self-generated predictions can lead to the rapid accumulation of errors over multiple steps, while using the actual observations introduces exposure bias as these values are unavailable during the extrapolation stage. In this regard, this study proposes a novel training approach called reinforced decoder, which introduces auxiliary models to generate alternative decoder inputs that remain accessible when extrapolating. Additionally, a reinforcement learning algorithm is utilized to dynamically select the optimal inputs to improve accuracy. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms representative training methods over several datasets. Furthermore, the proposed approach also exhibits promising performance when generalized to self-attention-based sequence-to-sequence forecasting models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge