Regularized Q-learning
Paper and Code
Mar 01, 2022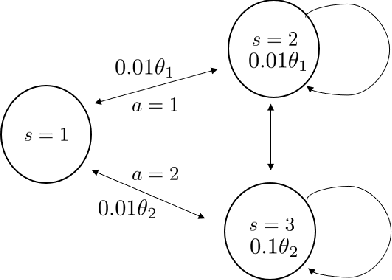
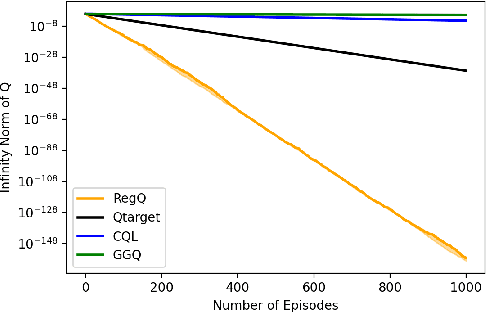
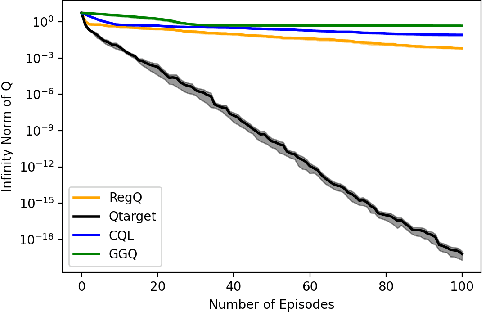
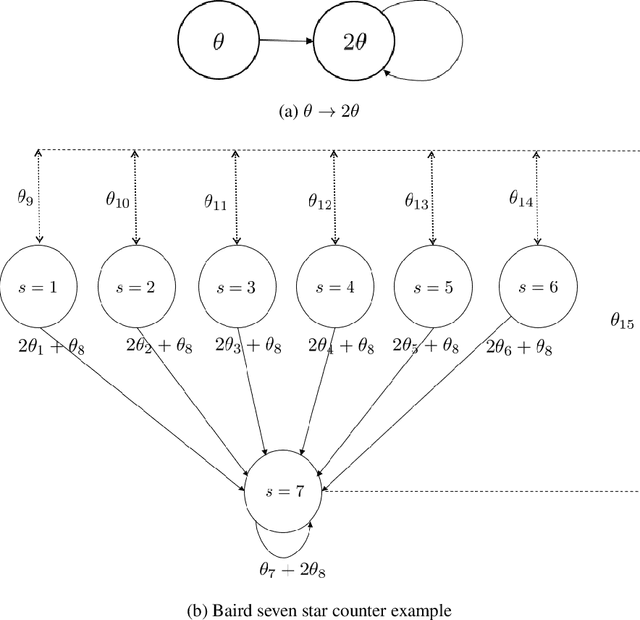
Q-learning is widely used algorithm in reinforcement learning community. Under the lookup table setting, its convergence is well established. However, its behavior is known to be unstable with the linear function approximation case. This paper develops a new Q-learning algorithm that converges when linear function approximation is used. We prove that simply adding an appropriate regularization term ensures convergence of the algorithm. We prove its stability using a recent analysis tool based on switching system models. Moreover, we experimentally show that it converges in environments where Q-learning with linear function approximation has known to diverge. We also provide an error bound on the solution where the algorithm converges.
* fix t->k
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge