Reducing Tactile Sim2Real Domain Gaps via Deep Texture Generation Networks
Paper and Code
Dec 03, 2021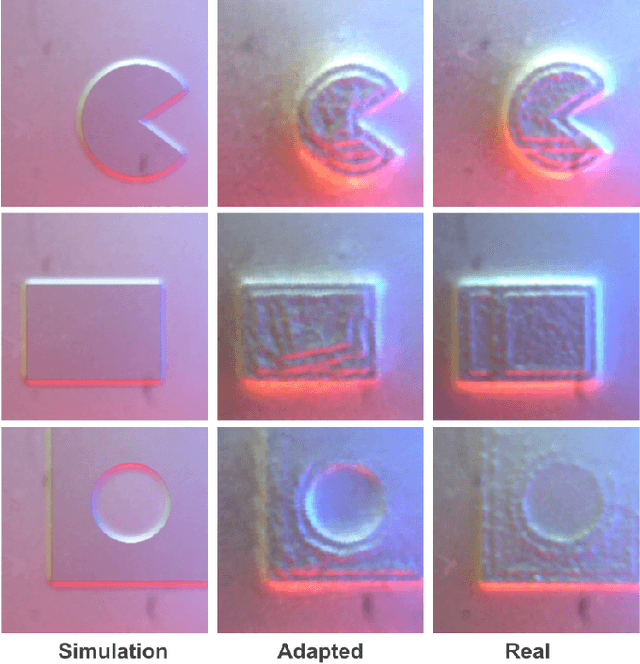
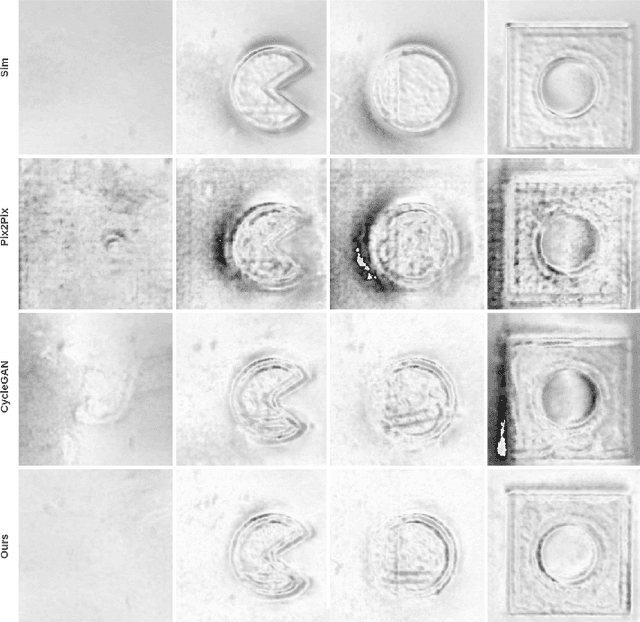
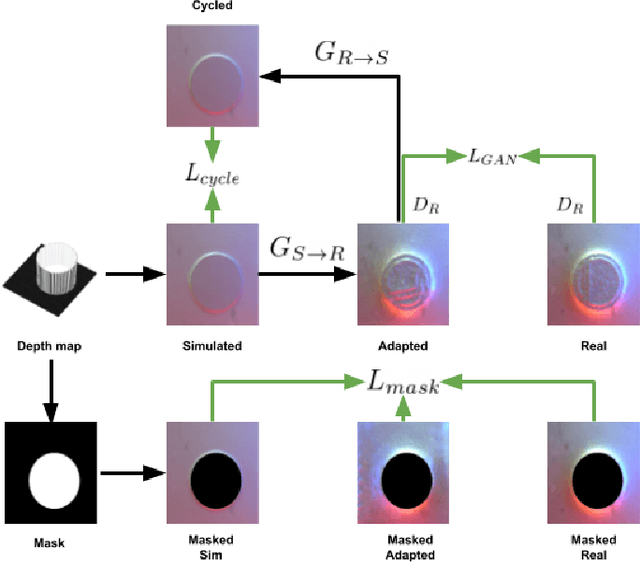


Recently simulation methods have been developed for optical tactile sensors to enable the Sim2Real learning, i.e., firstly training models in simulation before deploying them on the real robot. However, some artefacts in the real objects are unpredictable, such as imperfections caused by fabrication processes, or scratches by the natural wear and tear, and thus cannot be represented in the simulation, resulting in a significant gap between the simulated and real tactile images. To address this Sim2Real gap, we propose a novel texture generation network that maps the simulated images into photorealistic tactile images that resemble a real sensor contacting a real imperfect object. Each simulated tactile image is first divided into two types of regions: areas that are in contact with the object and areas that are not. The former is applied with generated textures learned from real textures in the real tactile images, whereas the latter maintains its appearance as when the sensor is not in contact with any object. This makes sure that the artefacts are only applied to the deformed regions of the sensor. Our extensive experiments show that the proposed texture generation network can generate these realistic artefacts on the deformed regions of the sensor, while avoiding leaking the textures into areas of no contact. Quantitative experiments further reveal that when using the adapted images generated by our proposed network for a Sim2Real classification task, the drop in accuracy caused by the Sim2Real gap is reduced from 38.43% to merely 0.81%. As such, this work has the potential to accelerate the Sim2Real learning for robotic tasks requiring tactile sensing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge