Rediscovering the Slavic Continuum in Representations Emerging from Neural Models of Spoken Language Identification
Paper and Code
Oct 22, 2020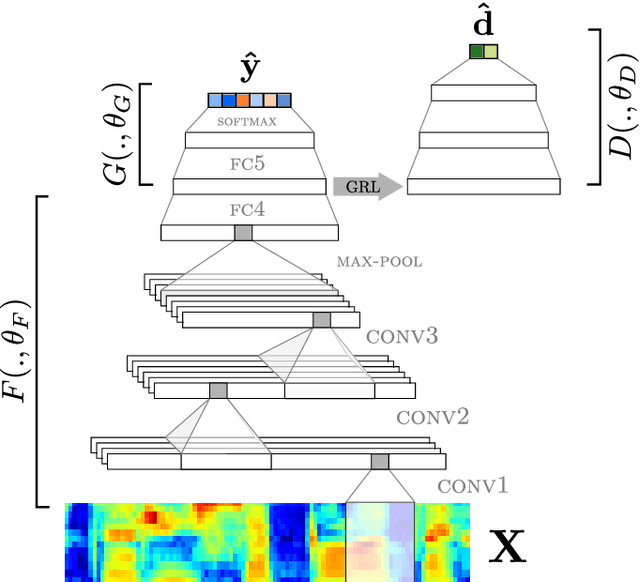
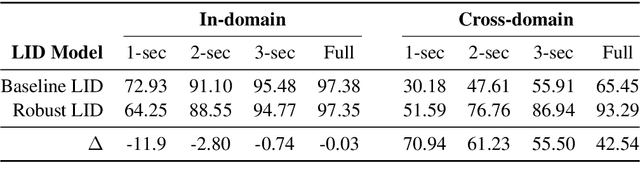
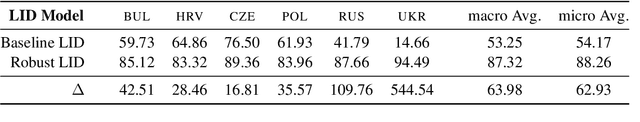
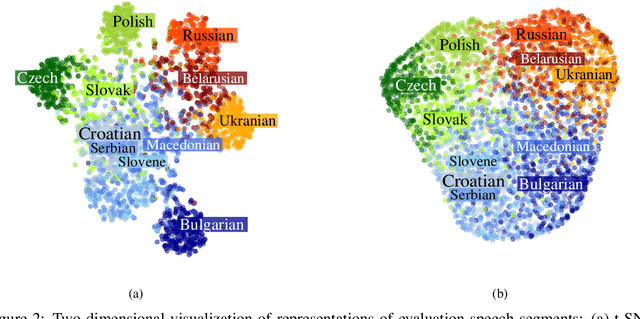
Deep neural networks have been employed for various spoken language recognition tasks, including tasks that are multilingual by definition such as spoken language identification. In this paper, we present a neural model for Slavic language identification in speech signals and analyze its emergent representations to investigate whether they reflect objective measures of language relatedness and/or non-linguists' perception of language similarity. While our analysis shows that the language representation space indeed captures language relatedness to a great extent, we find perceptual confusability between languages in our study to be the best predictor of the language representation similarity.
* Accepted in VarDial 2020 Workshop
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge