Recommender systems: when memory matters
Paper and Code
Dec 04, 2021

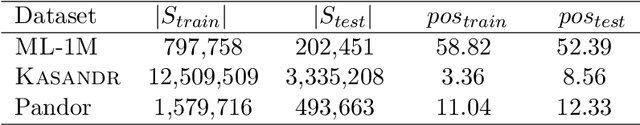
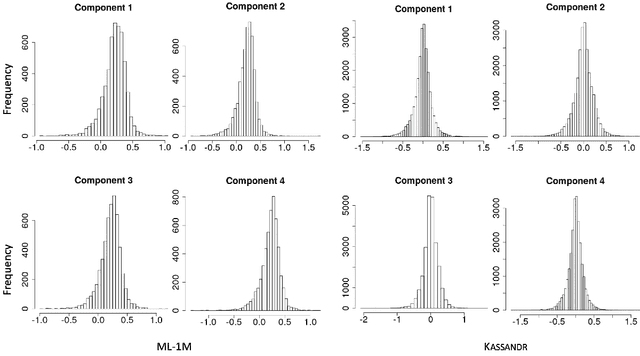
In this paper, we study the effect of long memory in the learnability of a sequential recommender system including users' implicit feedback. We propose an online algorithm, where model parameters are updated user per user over blocks of items constituted by a sequence of unclicked items followed by a clicked one. We illustrate through thorough empirical evaluations that filtering users with respect to the degree of long memory contained in their interactions with the system allows to substantially gain in performance with respect to MAP and NDCG, especially in the context of training large-scale Recommender Systems.
* Accepted to the 44-th European Conference on Information Retrieval
(ECIR), 2022. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2012.06910
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge