Recognize Foreign Low-Frequency Words with Similar Pairs
Paper and Code
Jun 16, 2015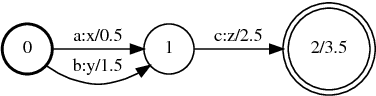
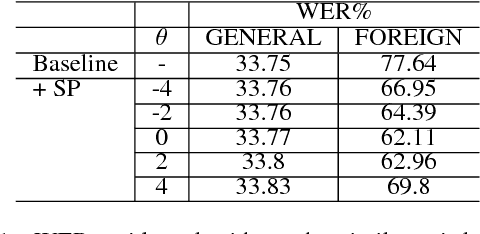
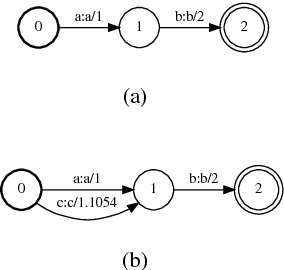
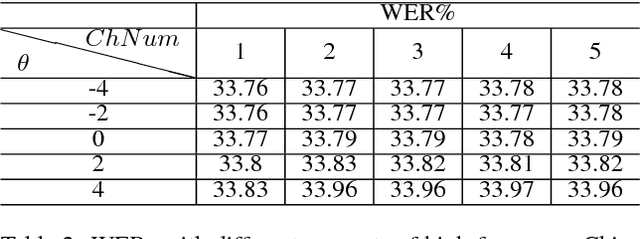
Low-frequency words place a major challenge for automatic speech recognition (ASR). The probabilities of these words, which are often important name entities, are generally under-estimated by the language model (LM) due to their limited occurrences in the training data. Recently, we proposed a word-pair approach to deal with the problem, which borrows information of frequent words to enhance the probabilities of low-frequency words. This paper presents an extension to the word-pair method by involving multiple `predicting words' to produce better estimation for low-frequency words. We also employ this approach to deal with out-of-language words in the task of multi-lingual speech recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge