Real-time monitoring of driver drowsiness on mobile platforms using 3D neural networks
Paper and Code
Oct 15, 2019
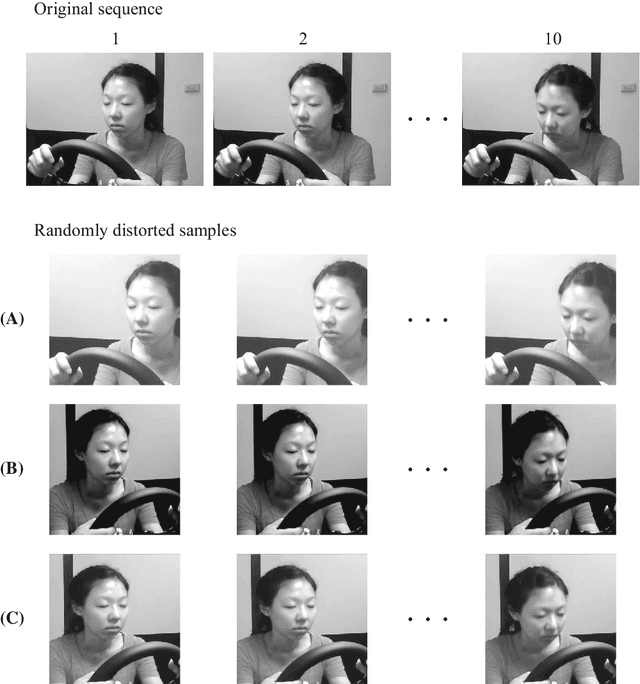

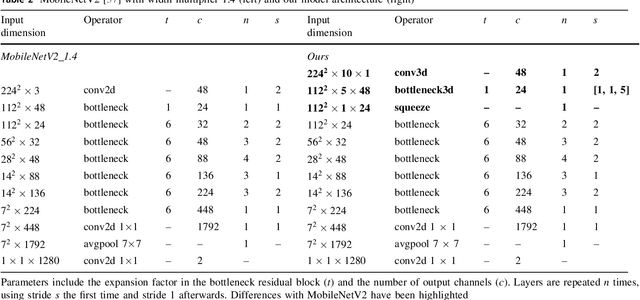
Driver drowsiness increases crash risk, leading to substantial road trauma each year. Drowsiness detection methods have received considerable attention, but few studies have investigated the implementation of a detection approach on a mobile phone. Phone applications reduce the need for specialised hardware and hence, enable a cost-effective roll-out of the technology across the driving population. While it has been shown that three-dimensional (3D) operations are more suitable for spatiotemporal feature learning, current methods for drowsiness detection commonly use frame-based, multi-step approaches. However, computationally expensive techniques that achieve superior results on action recognition benchmarks (e.g. 3D convolutions, optical flow extraction) create bottlenecks for real-time, safety-critical applications on mobile devices. Here, we show how depthwise separable 3D convolutions, combined with an early fusion of spatial and temporal information, can achieve a balance between high prediction accuracy and real-time inference requirements. In particular, increased accuracy is achieved when assessment requires motion information, for example, when sunglasses conceal the eyes. Further, a custom TensorFlow-based smartphone application shows the true impact of various approaches on inference times and demonstrates the effectiveness of real-time monitoring based on out-of-sample data to alert a drowsy driver. Our model is pre-trained on ImageNet and Kinetics and fine-tuned on a publicly available Driver Drowsiness Detection dataset. Fine-tuning on large naturalistic driving datasets could further improve accuracy to obtain robust in-vehicle performance. Overall, our research is a step towards practical deep learning applications, potentially preventing micro-sleeps and reducing road trauma.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge