Real-time Hyperspectral Imaging in Hardware via Trained Metasurface Encoders
Paper and Code
Apr 05, 2022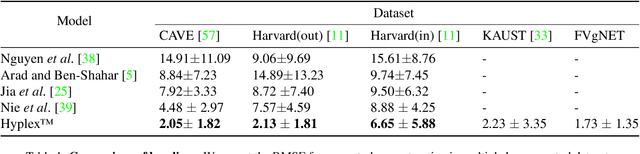

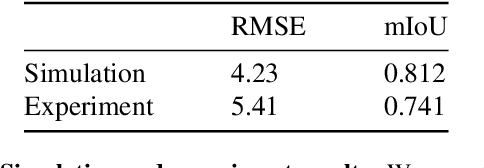
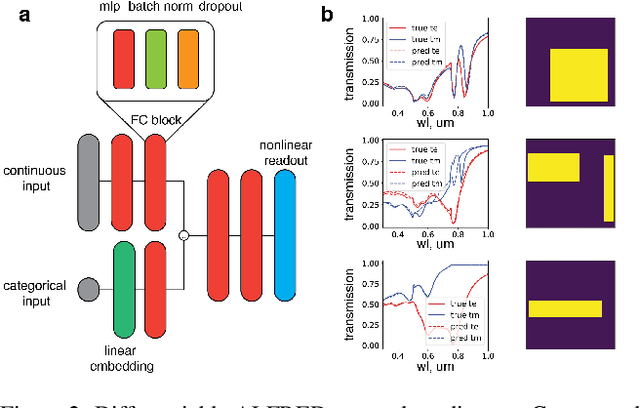
Hyperspectral imaging has attracted significant attention to identify spectral signatures for image classification and automated pattern recognition in computer vision. State-of-the-art implementations of snapshot hyperspectral imaging rely on bulky, non-integrated, and expensive optical elements, including lenses, spectrometers, and filters. These macroscopic components do not allow fast data processing for, e.g real-time and high-resolution videos. This work introduces Hyplex, a new integrated architecture addressing the limitations discussed above. Hyplex is a CMOS-compatible, fast hyperspectral camera that replaces bulk optics with nanoscale metasurfaces inversely designed through artificial intelligence. Hyplex does not require spectrometers but makes use of conventional monochrome cameras, opening up the possibility for real-time and high-resolution hyperspectral imaging at inexpensive costs. Hyplex exploits a model-driven optimization, which connects the physical metasurfaces layer with modern visual computing approaches based on end-to-end training. We design and implement a prototype version of Hyplex and compare its performance against the state-of-the-art for typical imaging tasks such as spectral reconstruction and semantic segmentation. In all benchmarks, Hyplex reports the smallest reconstruction error. We additionally present what is, to the best of our knowledge, the largest publicly available labeled hyperspectral dataset for semantic segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge