Real-Time GPU-Accelerated Machine Learning Based Multiuser Detection for 5G and Beyond
Paper and Code
Jan 14, 2022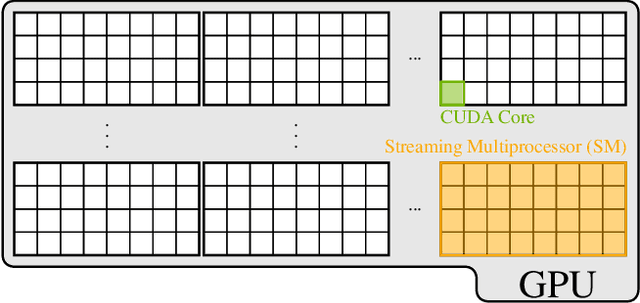
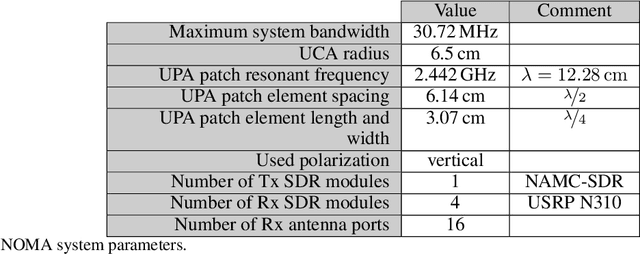
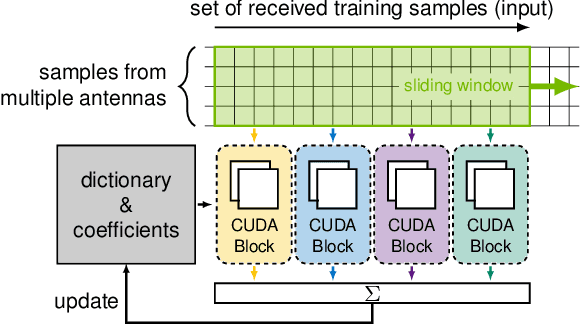
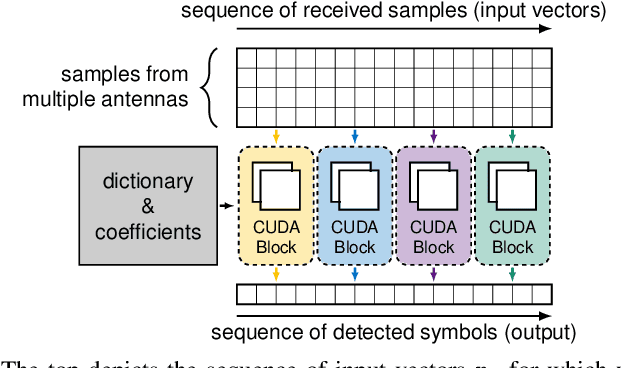
Adaptive partial linear beamforming meets the need of 5G and future 6G applications for high flexibility and adaptability. Choosing an appropriate tradeoff between conflicting goals opens the recently proposed multiuser (MU) detection method. Due to their high spatial resolution, nonlinear beamforming filters can significantly outperform linear approaches in stationary scenarios with massive connectivity. However, a dramatic decrease in performance can be expected in high mobility scenarios because they are very susceptible to changes in the wireless channel. The robustness of linear filters is required, considering these changes. One way to respond appropriately is to use online machine learning algorithms. The theory of algorithms based on the adaptive projected subgradient method (APSM) is rich, and they promise accurate tracking capabilities in dynamic wireless environments. However, one of the main challenges comes from the real-time implementation of these algorithms, which involve projections on time-varying closed convex sets. While the projection operations are relatively simple, their vast number poses a challenge in ultralow latency (ULL) applications where latency constraints must be satisfied in every radio frame. Taking non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) systems as an example, this paper explores the acceleration of APSM-based algorithms through massive parallelization. The result is a GPU-accelerated real-time implementation of an orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM)-based transceiver that enables detection latency of less than one millisecond and therefore complies with the requirements of 5G and beyond. To meet the stringent physical layer latency requirements, careful co-design of hardware and software is essential, especially in virtualized wireless systems with hardware accelerators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge