Ray Interference: a Source of Plateaus in Deep Reinforcement Learning
Paper and Code
Apr 25, 2019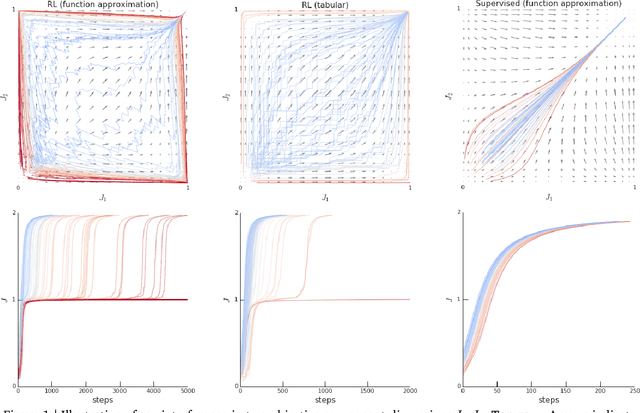
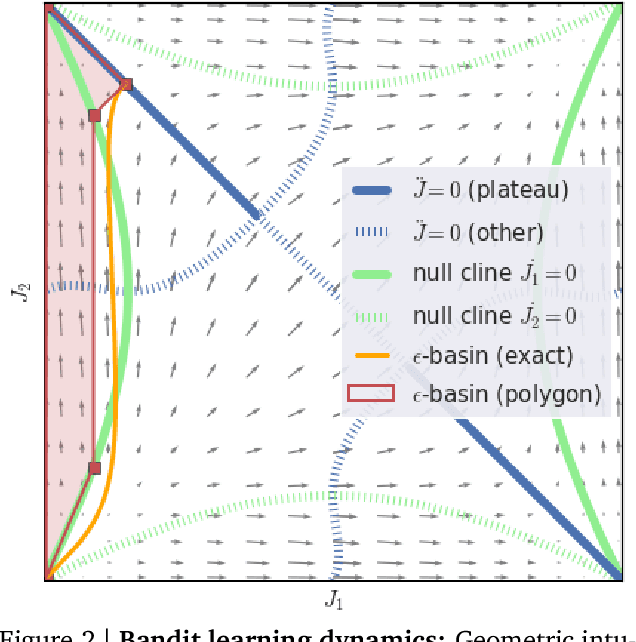
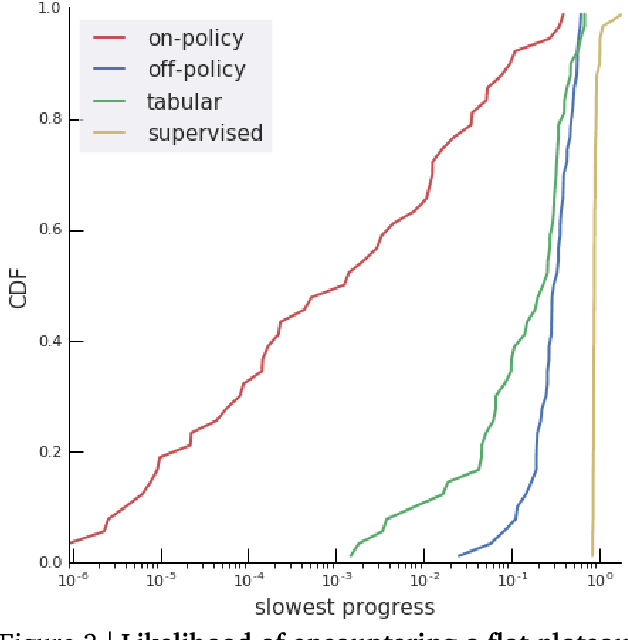
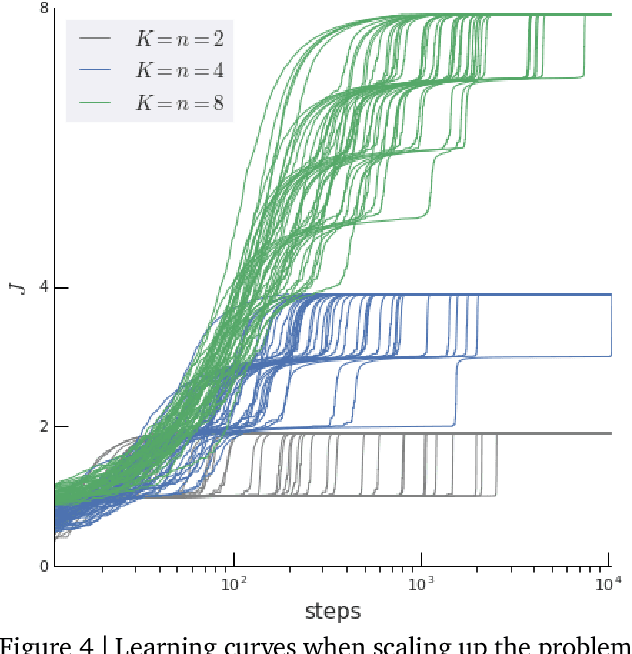
Rather than proposing a new method, this paper investigates an issue present in existing learning algorithms. We study the learning dynamics of reinforcement learning (RL), specifically a characteristic coupling between learning and data generation that arises because RL agents control their future data distribution. In the presence of function approximation, this coupling can lead to a problematic type of 'ray interference', characterized by learning dynamics that sequentially traverse a number of performance plateaus, effectively constraining the agent to learn one thing at a time even when learning in parallel is better. We establish the conditions under which ray interference occurs, show its relation to saddle points and obtain the exact learning dynamics in a restricted setting. We characterize a number of its properties and discuss possible remedies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge