Rank-to-engage: New Listwise Approaches to Maximize Engagement
Paper and Code
Feb 24, 2017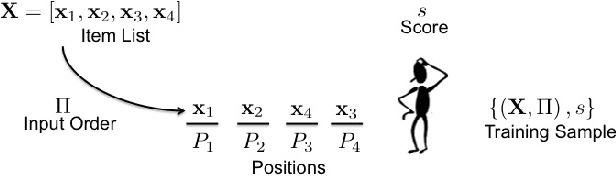

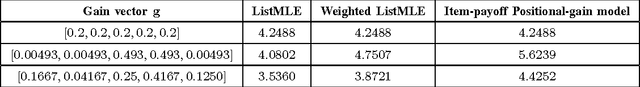
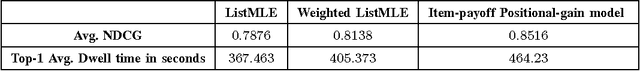
For many internet businesses, presenting a given list of items in an order that maximizes a certain metric of interest (e.g., click-through-rate, average engagement time etc.) is crucial. We approach the aforementioned task from a learning-to-rank perspective which reveals a new problem setup. In traditional learning-to-rank literature, it is implicitly assumed that during the training data generation one has access to the \emph{best or desired} order for the given list of items. In this work, we consider a problem setup where we do not observe the desired ranking. We present two novel solutions: the first solution is an extension of already existing listwise learning-to-rank technique--Listwise maximum likelihood estimation (ListMLE)--while the second one is a generic machine learning based framework that tackles the problem in its entire generality. We discuss several challenges associated with this generic framework, and propose a simple \emph{item-payoff} and \emph{positional-gain} model that addresses these challenges. We provide training algorithms, inference procedures, and demonstrate the effectiveness of the two approaches over traditional ListMLE on synthetic as well as on real-life setting of ranking news articles for increased dwell time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge