RadioMic: Sound Sensing via mmWave Signals
Paper and Code
Aug 06, 2021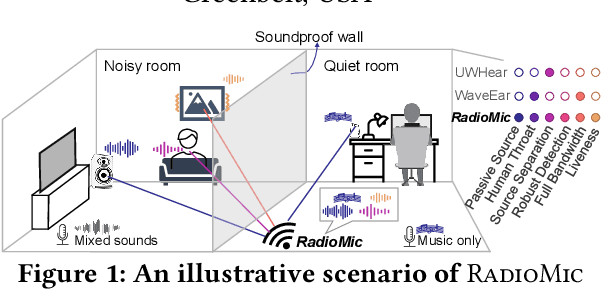
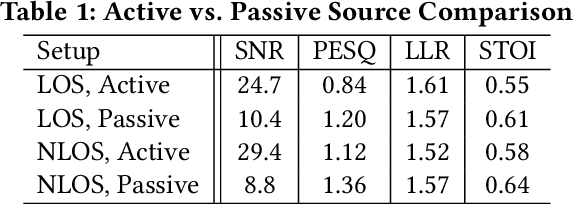
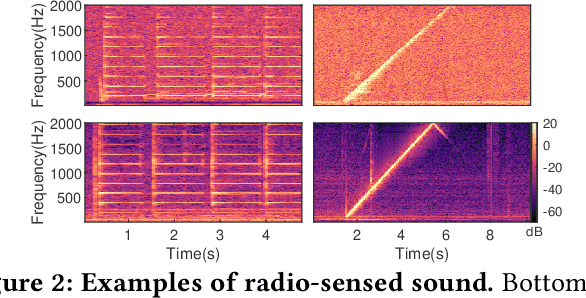
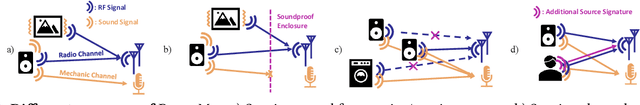
Voice interfaces has become an integral part of our lives, with the proliferation of smart devices. Today, IoT devices mainly rely on microphones to sense sound. Microphones, however, have fundamental limitations, such as weak source separation, limited range in the presence of acoustic insulation, and being prone to multiple side-channel attacks. In this paper, we propose RadioMic, a radio-based sound sensing system to mitigate these issues and enrich sound applications. RadioMic constructs sound based on tiny vibrations on active sources (e.g., a speaker or human throat) or object surfaces (e.g., paper bag), and can work through walls, even a soundproof one. To convert the extremely weak sound vibration in the radio signals into sound signals, RadioMic introduces radio acoustics, and presents training-free approaches for robust sound detection and high-fidelity sound recovery. It then exploits a neural network to further enhance the recovered sound by expanding the recoverable frequencies and reducing the noises. RadioMic translates massive online audios to synthesized data to train the network, and thus minimizes the need of RF data. We thoroughly evaluate RadioMic under different scenarios using a commodity mmWave radar. The results show RadioMic outperforms the state-of-the-art systems significantly. We believe RadioMic provides new horizons for sound sensing and inspires attractive sensing capabilities of mmWave sensing devices
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge