Quantifying Feature Contributions to Overall Disparity Using Information Theory
Paper and Code
Jun 16, 2022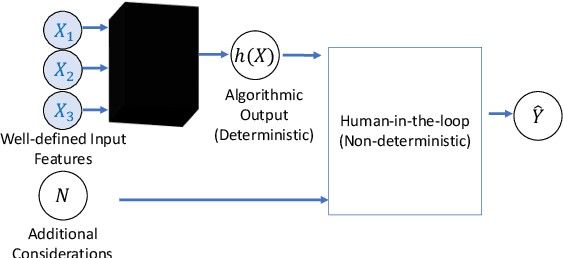
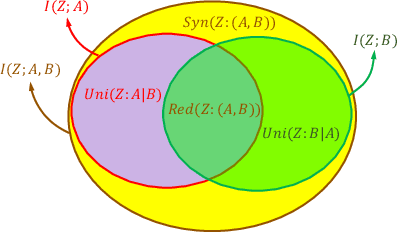
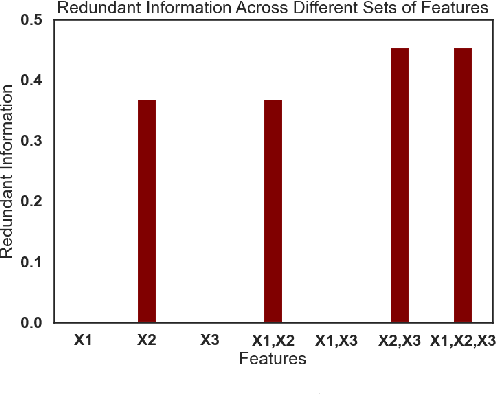

When a machine-learning algorithm makes biased decisions, it can be helpful to understand the sources of disparity to explain why the bias exists. Towards this, we examine the problem of quantifying the contribution of each individual feature to the observed disparity. If we have access to the decision-making model, one potential approach (inspired from intervention-based approaches in explainability literature) is to vary each individual feature (while keeping the others fixed) and use the resulting change in disparity to quantify its contribution. However, we may not have access to the model or be able to test/audit its outputs for individually varying features. Furthermore, the decision may not always be a deterministic function of the input features (e.g., with human-in-the-loop). For these situations, we might need to explain contributions using purely distributional (i.e., observational) techniques, rather than interventional. We ask the question: what is the "potential" contribution of each individual feature to the observed disparity in the decisions when the exact decision-making mechanism is not accessible? We first provide canonical examples (thought experiments) that help illustrate the difference between distributional and interventional approaches to explaining contributions, and when either is better suited. When unable to intervene on the inputs, we quantify the "redundant" statistical dependency about the protected attribute that is present in both the final decision and an individual feature, by leveraging a body of work in information theory called Partial Information Decomposition. We also perform a simple case study to show how this technique could be applied to quantify contributions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge