Quantifying Epistemic Uncertainty in Absolute Pose Regression
Paper and Code
Apr 09, 2025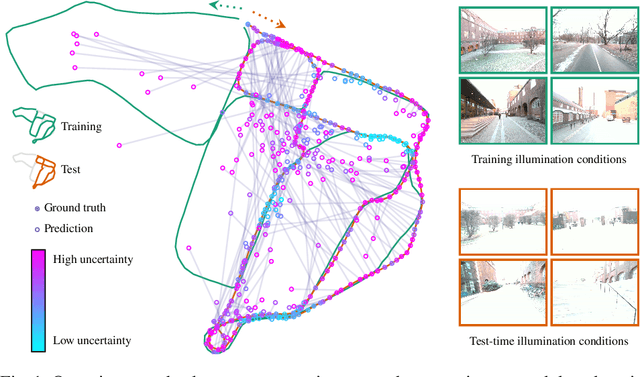
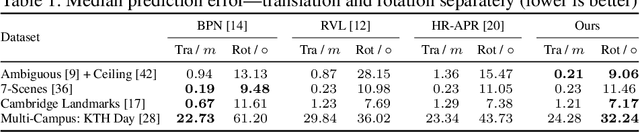
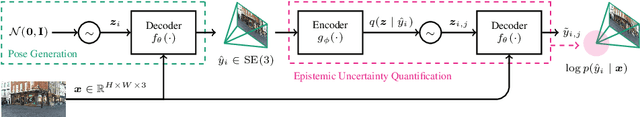
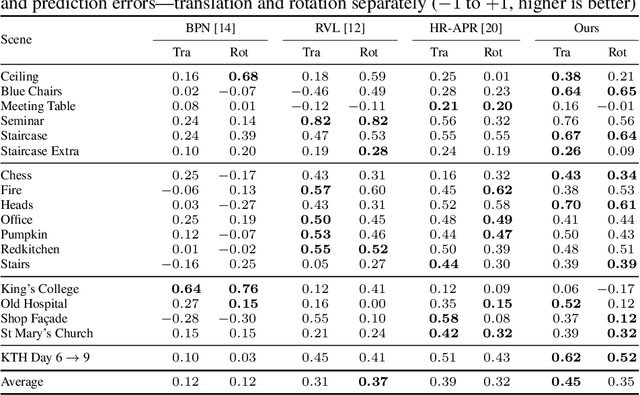
Visual relocalization is the task of estimating the camera pose given an image it views. Absolute pose regression offers a solution to this task by training a neural network, directly regressing the camera pose from image features. While an attractive solution in terms of memory and compute efficiency, absolute pose regression's predictions are inaccurate and unreliable outside the training domain. In this work, we propose a novel method for quantifying the epistemic uncertainty of an absolute pose regression model by estimating the likelihood of observations within a variational framework. Beyond providing a measure of confidence in predictions, our approach offers a unified model that also handles observation ambiguities, probabilistically localizing the camera in the presence of repetitive structures. Our method outperforms existing approaches in capturing the relation between uncertainty and prediction error.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge