Pursuing Feature Separation based on Neural Collapse for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Paper and Code
May 28, 2024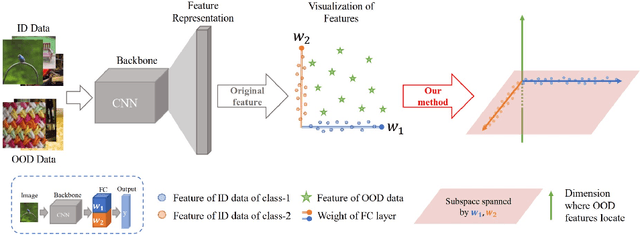



In the open world, detecting out-of-distribution (OOD) data, whose labels are disjoint with those of in-distribution (ID) samples, is important for reliable deep neural networks (DNNs). To achieve better detection performance, one type of approach proposes to fine-tune the model with auxiliary OOD datasets to amplify the difference between ID and OOD data through a separation loss defined on model outputs. However, none of these studies consider enlarging the feature disparity, which should be more effective compared to outputs. The main difficulty lies in the diversity of OOD samples, which makes it hard to describe their feature distribution, let alone design losses to separate them from ID features. In this paper, we neatly fence off the problem based on an aggregation property of ID features named Neural Collapse (NC). NC means that the penultimate features of ID samples within a class are nearly identical to the last layer weight of the corresponding class. Based on this property, we propose a simple but effective loss called OrthLoss, which binds the features of OOD data in a subspace orthogonal to the principal subspace of ID features formed by NC. In this way, the features of ID and OOD samples are separated by different dimensions. By optimizing the feature separation loss rather than purely enlarging output differences, our detection achieves SOTA performance on CIFAR benchmarks without any additional data augmentation or sampling, demonstrating the importance of feature separation in OOD detection. The code will be published.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge