ProtDAT: A Unified Framework for Protein Sequence Design from Any Protein Text Description
Paper and Code
Dec 05, 2024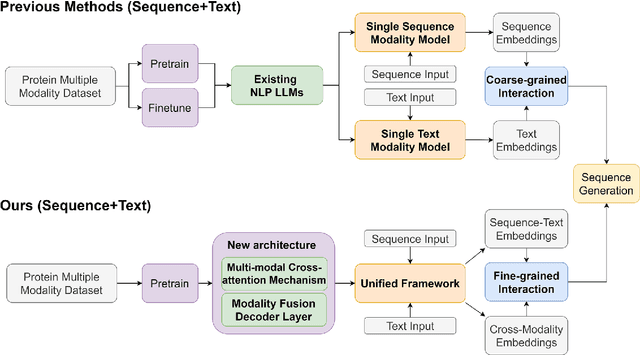
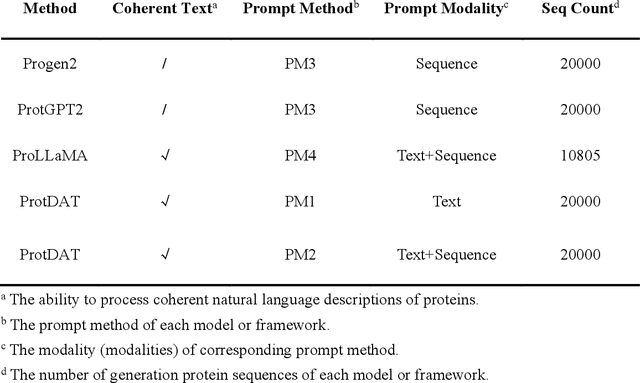
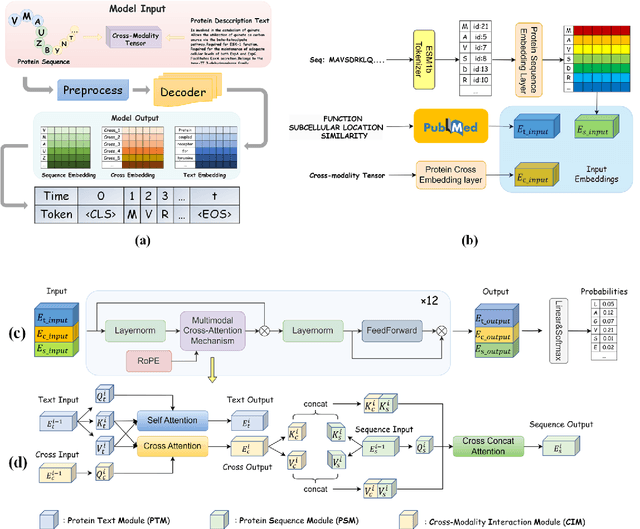
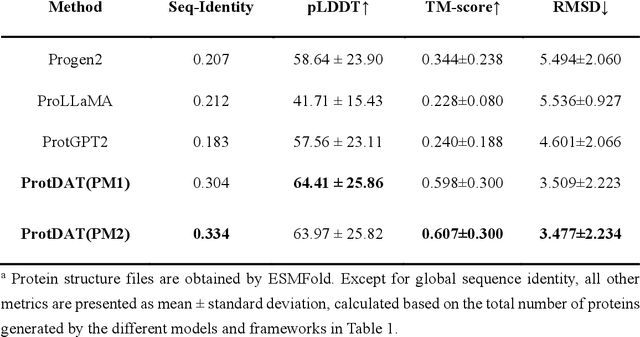
Protein design has become a critical method in advancing significant potential for various applications such as drug development and enzyme engineering. However, protein design methods utilizing large language models with solely pretraining and fine-tuning struggle to capture relationships in multi-modal protein data. To address this, we propose ProtDAT, a de novo fine-grained framework capable of designing proteins from any descriptive protein text input. ProtDAT builds upon the inherent characteristics of protein data to unify sequences and text as a cohesive whole rather than separate entities. It leverages an innovative multi-modal cross-attention, integrating protein sequences and textual information for a foundational level and seamless integration. Experimental results demonstrate that ProtDAT achieves the state-of-the-art performance in protein sequence generation, excelling in rationality, functionality, structural similarity, and validity. On 20,000 text-sequence pairs from Swiss-Prot, it improves pLDDT by 6%, TM-score by 0.26, and reduces RMSD by 1.2 {\AA}, highlighting its potential to advance protein design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge