Prompting Towards Alleviating Code-Switched Data Scarcity in Under-Resourced Languages with GPT as a Pivot
Paper and Code
Apr 26, 2024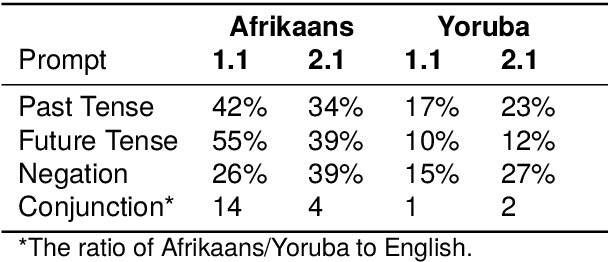
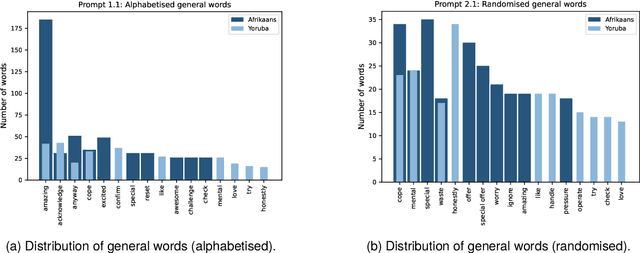
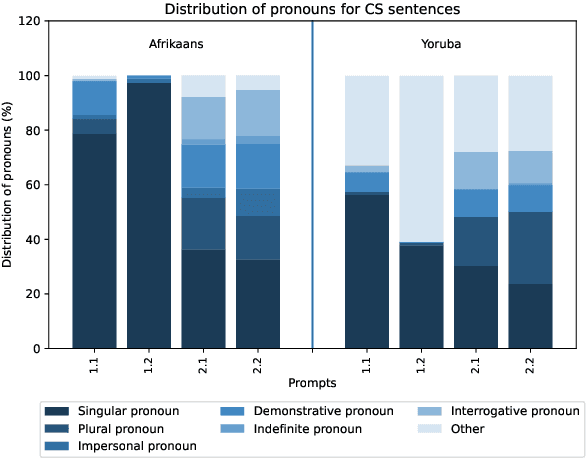
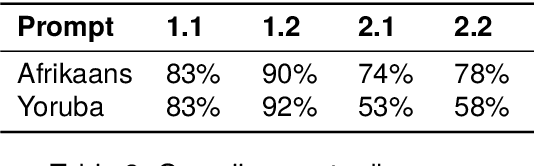
Many multilingual communities, including numerous in Africa, frequently engage in code-switching during conversations. This behaviour stresses the need for natural language processing technologies adept at processing code-switched text. However, data scarcity, particularly in African languages, poses a significant challenge, as many are low-resourced and under-represented. In this study, we prompted GPT 3.5 to generate Afrikaans--English and Yoruba--English code-switched sentences, enhancing diversity using topic-keyword pairs, linguistic guidelines, and few-shot examples. Our findings indicate that the quality of generated sentences for languages using non-Latin scripts, like Yoruba, is considerably lower when compared with the high Afrikaans-English success rate. There is therefore a notable opportunity to refine prompting guidelines to yield sentences suitable for the fine-tuning of language models. We propose a framework for augmenting the diversity of synthetically generated code-switched data using GPT and propose leveraging this technology to mitigate data scarcity in low-resourced languages, underscoring the essential role of native speakers in this process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge