Process-oriented Iterative Multiple Alignment for Medical Process Mining
Paper and Code
Sep 16, 2017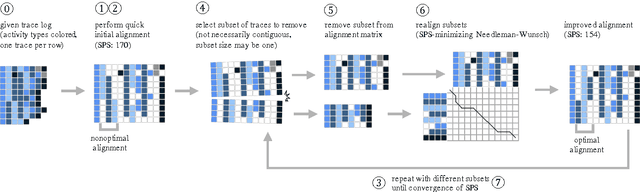
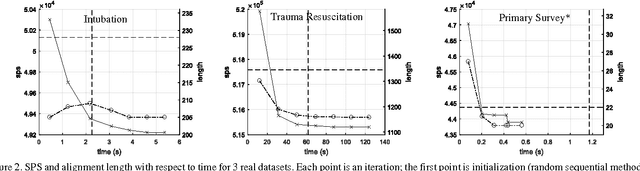
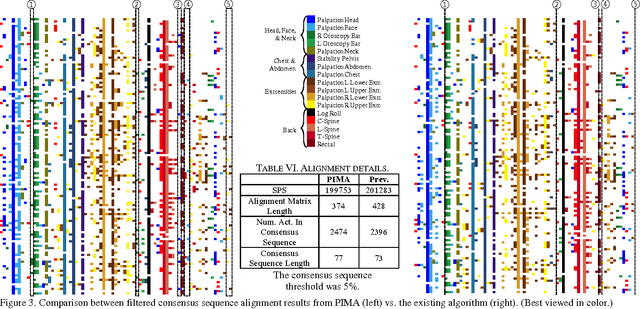
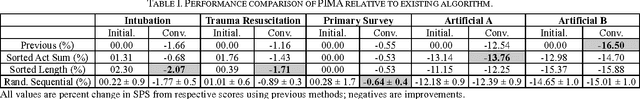
Adapted from biological sequence alignment, trace alignment is a process mining technique used to visualize and analyze workflow data. Any analysis done with this method, however, is affected by the alignment quality. The best existing trace alignment techniques use progressive guide-trees to heuristically approximate the optimal alignment in O(N2L2) time. These algorithms are heavily dependent on the selected guide-tree metric, often return sum-of-pairs-score-reducing errors that interfere with interpretation, and are computationally intensive for large datasets. To alleviate these issues, we propose process-oriented iterative multiple alignment (PIMA), which contains specialized optimizations to better handle workflow data. We demonstrate that PIMA is a flexible framework capable of achieving better sum-of-pairs score than existing trace alignment algorithms in only O(NL2) time. We applied PIMA to analyzing medical workflow data, showing how iterative alignment can better represent the data and facilitate the extraction of insights from data visualization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge