Probing Representation Forgetting in Supervised and Unsupervised Continual Learning
Paper and Code
Apr 05, 2022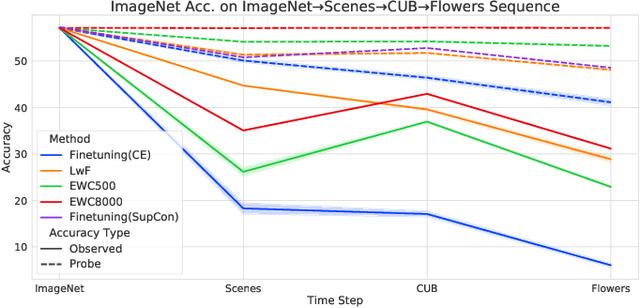
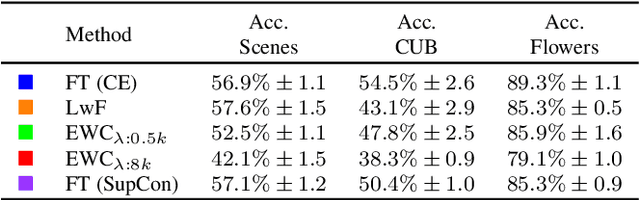
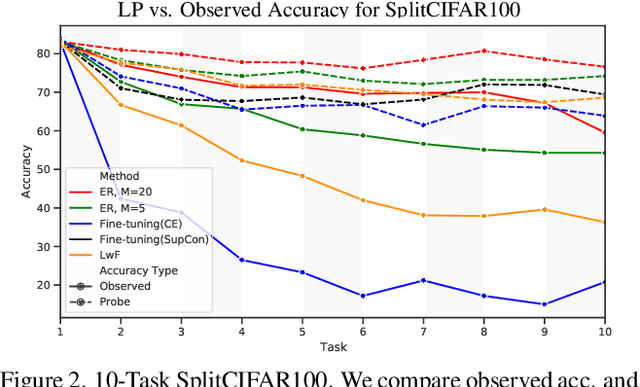
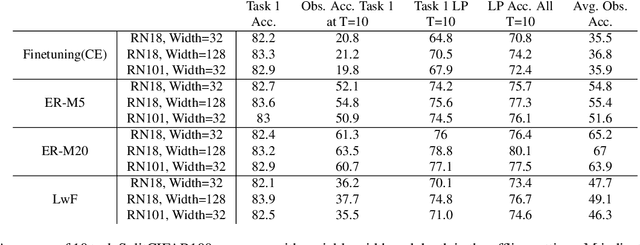
Continual Learning research typically focuses on tackling the phenomenon of catastrophic forgetting in neural networks. Catastrophic forgetting is associated with an abrupt loss of knowledge previously learned by a model when the task, or more broadly the data distribution, being trained on changes. In supervised learning problems this forgetting, resulting from a change in the model's representation, is typically measured or observed by evaluating the decrease in old task performance. However, a model's representation can change without losing knowledge about prior tasks. In this work we consider the concept of representation forgetting, observed by using the difference in performance of an optimal linear classifier before and after a new task is introduced. Using this tool we revisit a number of standard continual learning benchmarks and observe that, through this lens, model representations trained without any explicit control for forgetting often experience small representation forgetting and can sometimes be comparable to methods which explicitly control for forgetting, especially in longer task sequences. We also show that representation forgetting can lead to new insights on the effect of model capacity and loss function used in continual learning. Based on our results, we show that a simple yet competitive approach is to learn representations continually with standard supervised contrastive learning while constructing prototypes of class samples when queried on old samples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge