Principles of Designing Robust Remote Face Anti-Spoofing Systems
Paper and Code
Jun 06, 2024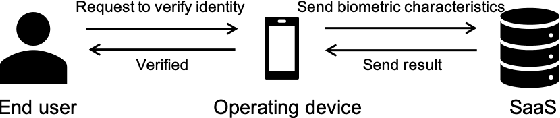

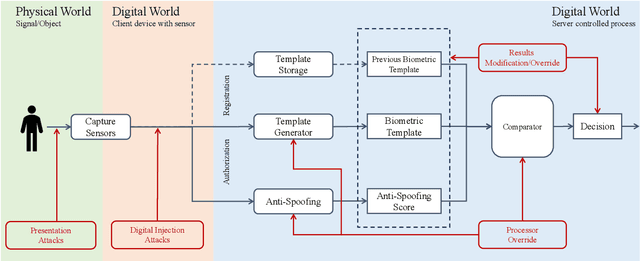

Protecting digital identities of human face from various attack vectors is paramount, and face anti-spoofing plays a crucial role in this endeavor. Current approaches primarily focus on detecting spoofing attempts within individual frames to detect presentation attacks. However, the emergence of hyper-realistic generative models capable of real-time operation has heightened the risk of digitally generated attacks. In light of these evolving threats, this paper aims to address two key aspects. First, it sheds light on the vulnerabilities of state-of-the-art face anti-spoofing methods against digital attacks. Second, it presents a comprehensive taxonomy of common threats encountered in face anti-spoofing systems. Through a series of experiments, we demonstrate the limitations of current face anti-spoofing detection techniques and their failure to generalize to novel digital attack scenarios. Notably, the existing models struggle with digital injection attacks including adversarial noise, realistic deepfake attacks, and digital replay attacks. To aid in the design and implementation of robust face anti-spoofing systems resilient to these emerging vulnerabilities, the paper proposes key design principles from model accuracy and robustness to pipeline robustness and even platform robustness. Especially, we suggest to implement the proactive face anti-spoofing system using active sensors to significant reduce the risks for unseen attack vectors and improve the user experience.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge