Preserving Domain Private Representation via Mutual Information Maximization
Paper and Code
Jan 09, 2022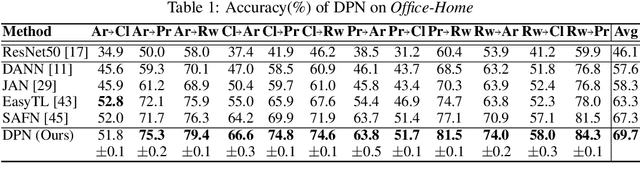
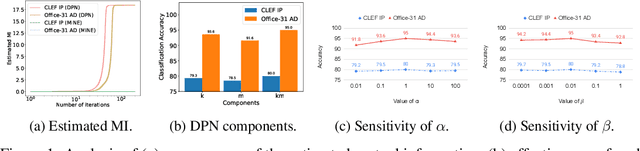
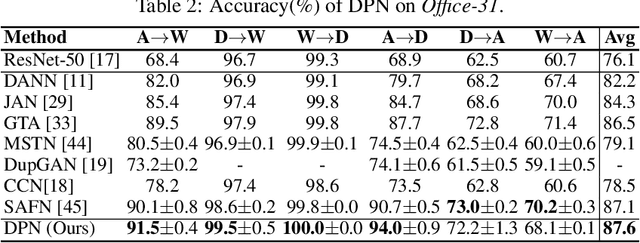
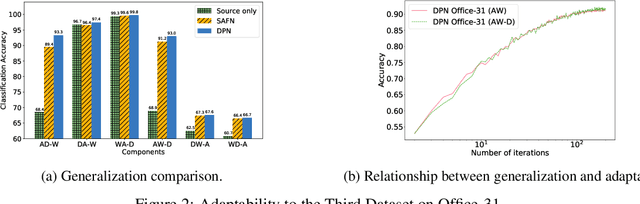
Recent advances in unsupervised domain adaptation have shown that mitigating the domain divergence by extracting the domain-invariant representation could significantly improve the generalization of a model to an unlabeled data domain. Nevertheless, the existing methods fail to effectively preserve the representation that is private to the label-missing domain, which could adversely affect the generalization. In this paper, we propose an approach to preserve such representation so that the latent distribution of the unlabeled domain could represent both the domain-invariant features and the individual characteristics that are private to the unlabeled domain. In particular, we demonstrate that maximizing the mutual information between the unlabeled domain and its latent space while mitigating the domain divergence can achieve such preservation. We also theoretically and empirically validate that preserving the representation that is private to the unlabeled domain is important and of necessity for the cross-domain generalization. Our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods on several public datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge