Predicting the Binding of SARS-CoV-2 Peptides to the Major Histocompatibility Complex with Recurrent Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Apr 16, 2021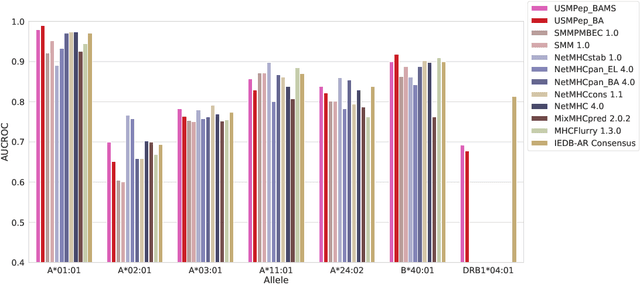
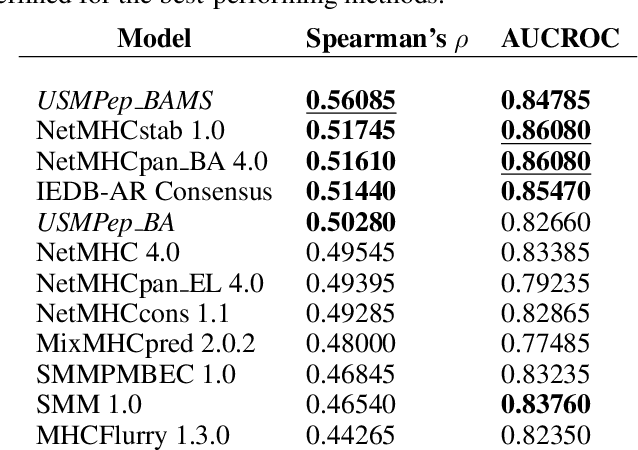
Predicting the binding of viral peptides to the major histocompatibility complex with machine learning can potentially extend the computational immunology toolkit for vaccine development, and serve as a key component in the fight against a pandemic. In this work, we adapt and extend USMPep, a recently proposed, conceptually simple prediction algorithm based on recurrent neural networks. Most notably, we combine regressors (binding affinity data) and classifiers (mass spectrometry data) from qualitatively different data sources to obtain a more comprehensive prediction tool. We evaluate the performance on a recently released SARS-CoV-2 dataset with binding stability measurements. USMPep not only sets new benchmarks on selected single alleles, but consistently turns out to be among the best-performing methods or, for some metrics, to be even the overall best-performing method for this task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge