Position: Editing Large Language Models Poses Serious Safety Risks
Paper and Code
Feb 05, 2025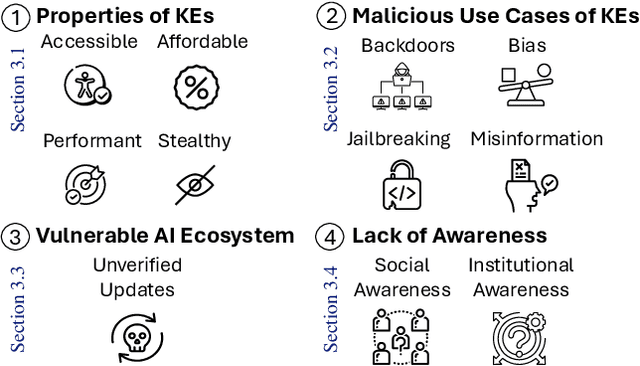



Large Language Models (LLMs) contain large amounts of facts about the world. These facts can become outdated over time, which has led to the development of knowledge editing methods (KEs) that can change specific facts in LLMs with limited side effects. This position paper argues that editing LLMs poses serious safety risks that have been largely overlooked. First, we note the fact that KEs are widely available, computationally inexpensive, highly performant, and stealthy makes them an attractive tool for malicious actors. Second, we discuss malicious use cases of KEs, showing how KEs can be easily adapted for a variety of malicious purposes. Third, we highlight vulnerabilities in the AI ecosystem that allow unrestricted uploading and downloading of updated models without verification. Fourth, we argue that a lack of social and institutional awareness exacerbates this risk, and discuss the implications for different stakeholders. We call on the community to (i) research tamper-resistant models and countermeasures against malicious model editing, and (ii) actively engage in securing the AI ecosystem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge