Pose Discrepancy Spatial Transformer Based Feature Disentangling for Partial Aspect Angles SAR Target Recognition
Paper and Code
Mar 07, 2021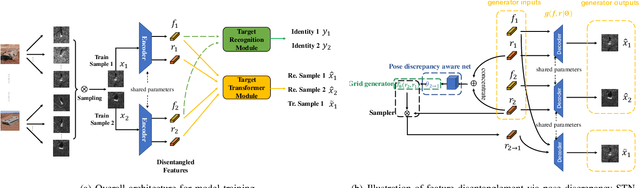
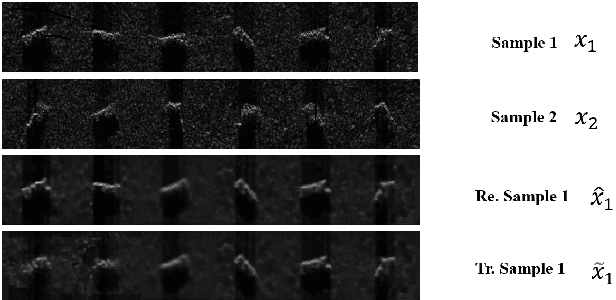
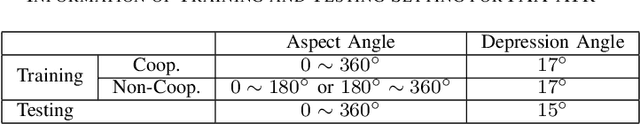
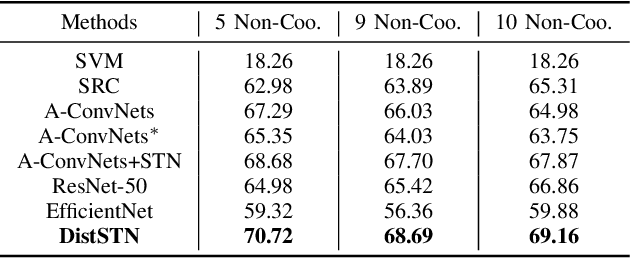
This letter presents a novel framework termed DistSTN for the task of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) automatic target recognition (ATR). In contrast to the conventional SAR ATR algorithms, DistSTN considers a more challenging practical scenario for non-cooperative targets whose aspect angles for training are incomplete and limited in a partial range while those of testing samples are unlimited. To address this issue, instead of learning the pose invariant features, DistSTN newly involves an elaborated feature disentangling model to separate the learned pose factors of a SAR target from the identity ones so that they can independently control the representation process of the target image. To disentangle the explainable pose factors, we develop a pose discrepancy spatial transformer module in DistSTN to characterize the intrinsic transformation between the factors of two different targets with an explicit geometric model. Furthermore, DistSTN develops an amortized inference scheme that enables efficient feature extraction and recognition using an encoder-decoder mechanism. Experimental results with the moving and stationary target acquisition and recognition (MSTAR) benchmark demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach. Compared with the other ATR algorithms, DistSTN can achieve higher recognition accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge