Planning with Partial Preference Models
Paper and Code
Jan 12, 2011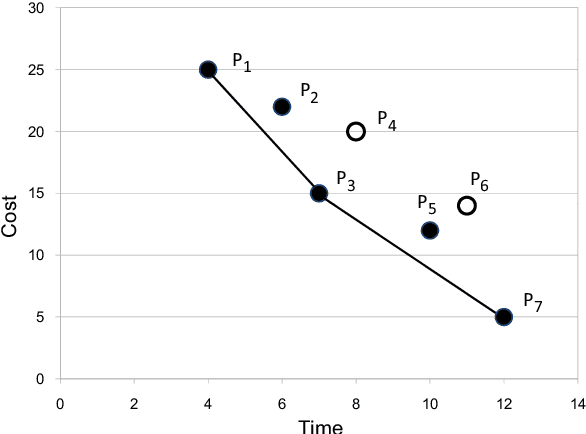
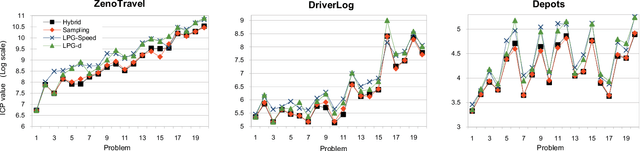
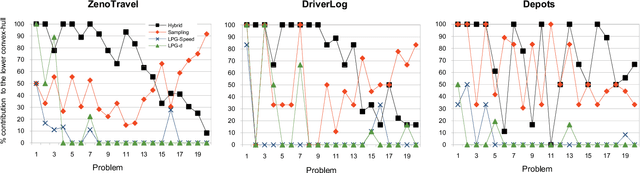
Current work in planning with preferences assume that the user's preference models are completely specified and aim to search for a single solution plan. In many real-world planning scenarios, however, the user probably cannot provide any information about her desired plans, or in some cases can only express partial preferences. In such situations, the planner has to present not only one but a set of plans to the user, with the hope that some of them are similar to the plan she prefers. We first propose the usage of different measures to capture quality of plan sets that are suitable for such scenarios: domain-independent distance measures defined based on plan elements (actions, states, causal links) if no knowledge of the user's preferences is given, and the Integrated Convex Preference measure in case the user's partial preference is provided. We then investigate various heuristic approaches to find set of plans according to these measures, and present empirical results demonstrating the promise of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge