Place recognition survey: An update on deep learning approaches
Paper and Code
Jun 22, 2021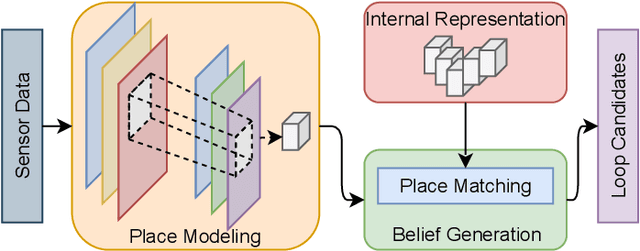

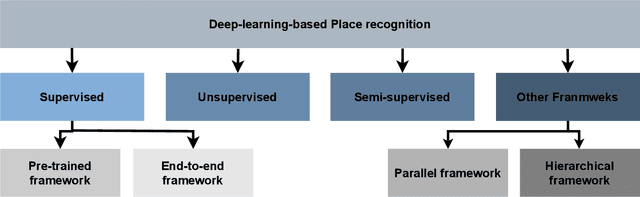
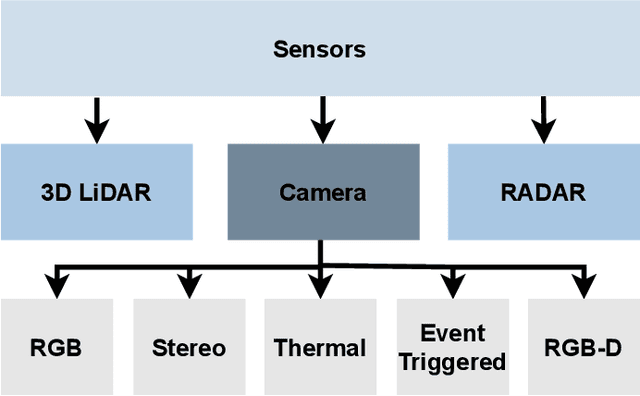
Autonomous Vehicles (AV) are becoming more capable of navigating in complex environments with dynamic and changing conditions. A key component that enables these intelligent vehicles to overcome such conditions and become more autonomous is the sophistication of the perception and localization systems. As part of the localization system, place recognition has benefited from recent developments in other perception tasks such as place categorization or object recognition, namely with the emergence of deep learning (DL) frameworks. This paper surveys recent approaches and methods used in place recognition, particularly those based on deep learning. The contributions of this work are twofold: surveying recent sensors such as 3D LiDARs and RADARs, applied in place recognition; and categorizing the various DL-based place recognition works into supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, parallel, and hierarchical categories. First, this survey introduces key place recognition concepts to contextualize the reader. Then, sensor characteristics are addressed. This survey proceeds by elaborating on the various DL-based works, presenting summaries for each framework. Some lessons learned from this survey include: the importance of NetVLAD for supervised end-to-end learning; the advantages of unsupervised approaches in place recognition, namely for cross-domain applications; or the increasing tendency of recent works to seek, not only for higher performance but also for higher efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge