PIDLoc: Cross-View Pose Optimization Network Inspired by PID Controllers
Paper and Code
Mar 04, 2025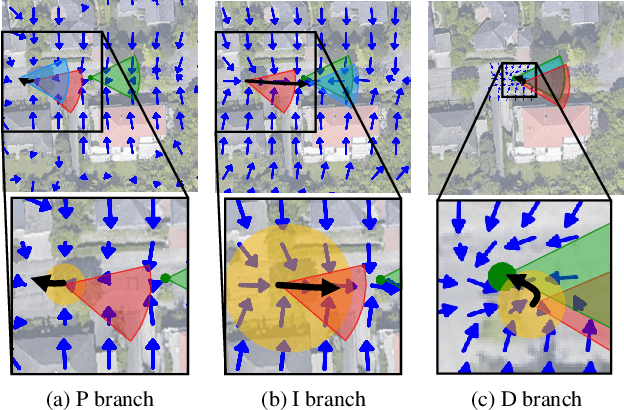
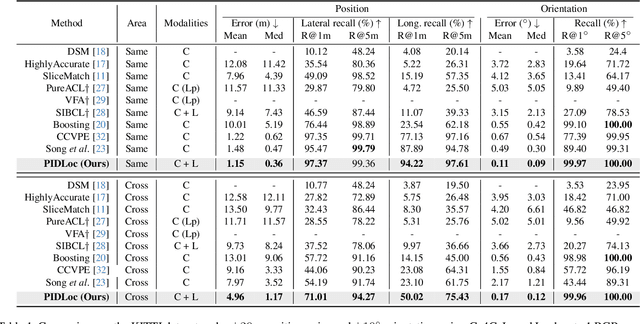
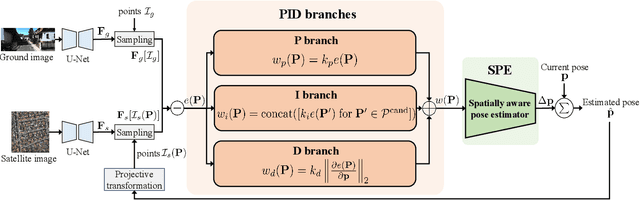
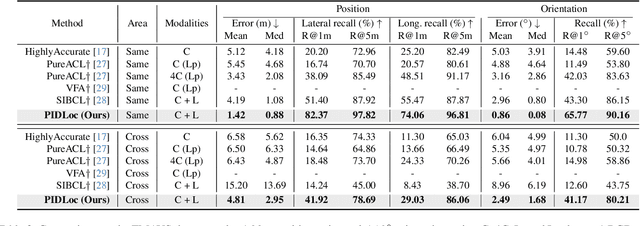
Accurate localization is essential for autonomous driving, but GNSS-based methods struggle in challenging environments such as urban canyons. Cross-view pose optimization offers an effective solution by directly estimating vehicle pose using satellite-view images. However, existing methods primarily rely on cross-view features at a given pose, neglecting fine-grained contexts for precision and global contexts for robustness against large initial pose errors. To overcome these limitations, we propose PIDLoc, a novel cross-view pose optimization approach inspired by the proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller. Using RGB images and LiDAR, the PIDLoc comprises the PID branches to model cross-view feature relationships and the spatially aware pose estimator (SPE) to estimate the pose from these relationships. The PID branches leverage feature differences for local context (P), aggregated feature differences for global context (I), and gradients of feature differences for precise pose adjustment (D) to enhance localization accuracy under large initial pose errors. Integrated with the PID branches, the SPE captures spatial relationships within the PID-branch features for consistent localization. Experimental results demonstrate that the PIDLoc achieves state-of-the-art performance in cross-view pose estimation for the KITTI dataset, reducing position error by $37.8\%$ compared with the previous state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge