Phrase-Level Class based Language Model for Mandarin Smart Speaker Query Recognition
Paper and Code
Sep 02, 2019
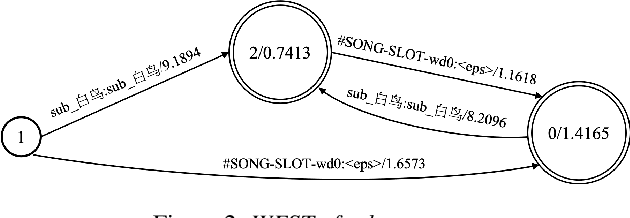
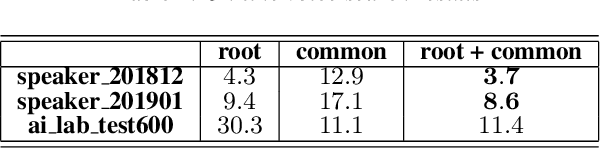
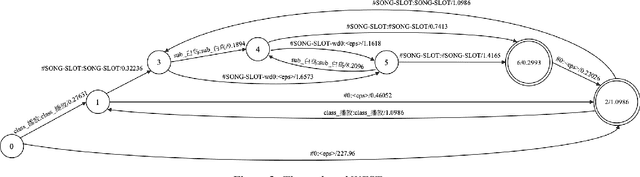
The success of speech assistants requires precise recognition of a number of entities on particular contexts. A common solution is to train a class-based n-gram language model and then expand the classes into specific words or phrases. However, when the class has a huge list, e.g., more than 20 million songs, a fully expansion will cause memory explosion. Worse still, the list items in the class need to be updated frequently, which requires a dynamic model updating technique. In this work, we propose to train pruned language models for the word classes to replace the slots in the root n-gram. We further propose to use a novel technique, named Difference Language Model (DLM), to correct the bias from the pruned language models. Once the decoding graph is built, we only need to recalculate the DLM when the entities in word classes are updated. Results show that the proposed method consistently and significantly outperforms the conventional approaches on all datasets, esp. for large lists, which the conventional approaches cannot handle.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge