PhishDef: URL Names Say It All
Paper and Code
Sep 12, 2010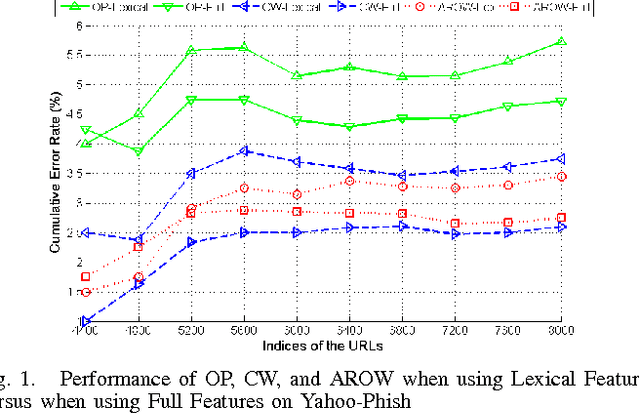
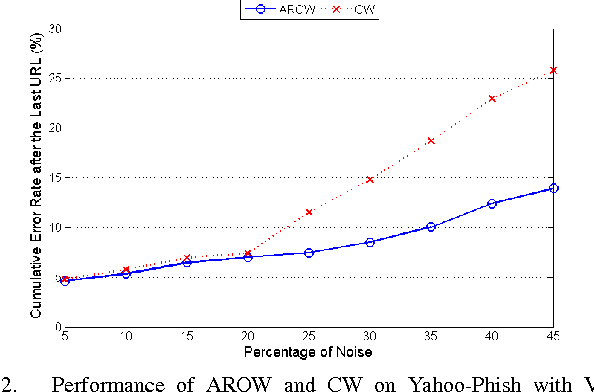
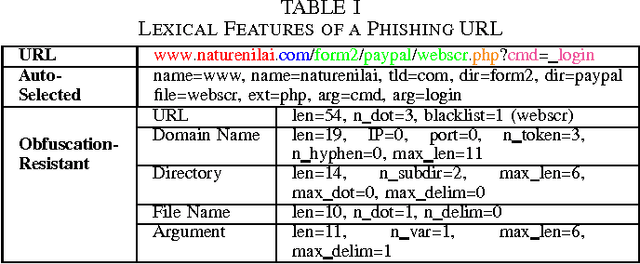
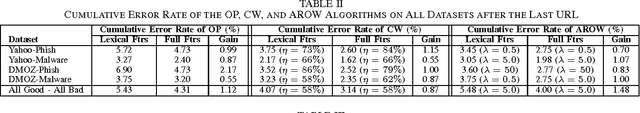
Phishing is an increasingly sophisticated method to steal personal user information using sites that pretend to be legitimate. In this paper, we take the following steps to identify phishing URLs. First, we carefully select lexical features of the URLs that are resistant to obfuscation techniques used by attackers. Second, we evaluate the classification accuracy when using only lexical features, both automatically and hand-selected, vs. when using additional features. We show that lexical features are sufficient for all practical purposes. Third, we thoroughly compare several classification algorithms, and we propose to use an online method (AROW) that is able to overcome noisy training data. Based on the insights gained from our analysis, we propose PhishDef, a phishing detection system that uses only URL names and combines the above three elements. PhishDef is a highly accurate method (when compared to state-of-the-art approaches over real datasets), lightweight (thus appropriate for online and client-side deployment), proactive (based on online classification rather than blacklists), and resilient to training data inaccuracies (thus enabling the use of large noisy training data).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge