Performance Advantages of Deep Neural Networks for Angle of Arrival Estimation
Paper and Code
Feb 17, 2019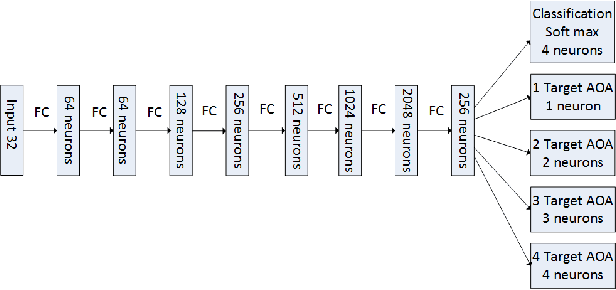
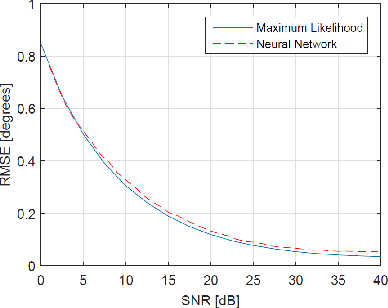


The problem of estimating the number of sources and their angles of arrival from a single antenna array observation has been an active area of research in the signal processing community for the last few decades. When the number of sources is large, the maximum likelihood estimator is intractable due to its very high complexity, and therefore alternative signal processing methods have been developed with some performance loss. In this paper, we apply a deep neural network (DNN) approach to the problem and analyze its advantages with respect to signal processing algorithms. We show that an appropriate designed network can attain the maximum likelihood performance with feasible complexity and outperform other feasible signal processing estimation methods over various signal to noise ratios and array response inaccuracies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge