Pay Attention to Hidden States for Video Deblurring: Ping-Pong Recurrent Neural Networks and Selective Non-Local Attention
Paper and Code
Apr 07, 2022
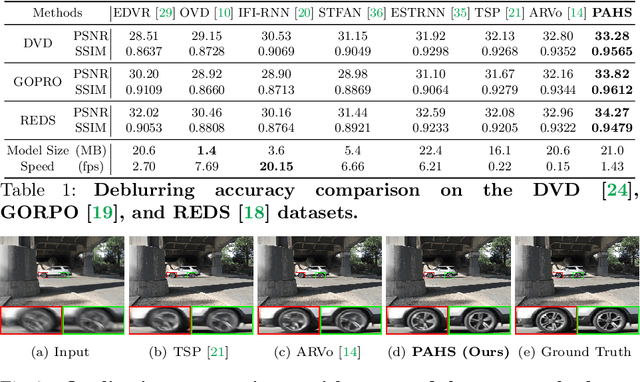
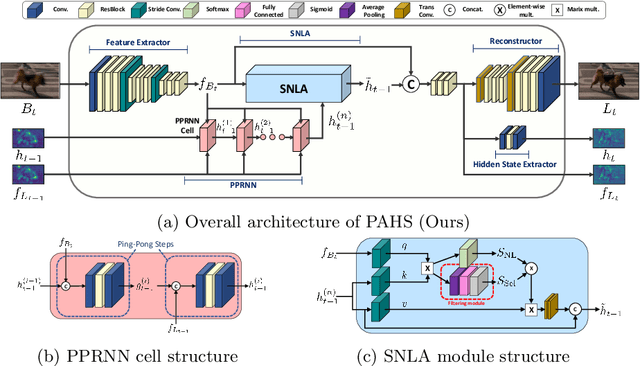

Video deblurring models exploit information in the neighboring frames to remove blur caused by the motion of the camera and the objects. Recurrent Neural Networks~(RNNs) are often adopted to model the temporal dependency between frames via hidden states. When motion blur is strong, however, hidden states are hard to deliver proper information due to the displacement between different frames. While there have been attempts to update the hidden states, it is difficult to handle misaligned features beyond the receptive field of simple modules. Thus, we propose 2 modules to supplement the RNN architecture for video deblurring. First, we design Ping-Pong RNN~(PPRNN) that acts on updating the hidden states by referring to the features from the current and the previous time steps alternately. PPRNN gathers relevant information from the both features in an iterative and balanced manner by utilizing its recurrent architecture. Second, we use a Selective Non-Local Attention~(SNLA) module to additionally refine the hidden state by aligning it with the positional information from the input frame feature. The attention score is scaled by the relevance to the input feature to focus on the necessary information. By paying attention to hidden states with both modules, which have strong synergy, our PAHS framework improves the representation powers of RNN structures and achieves state-of-the-art deblurring performance on standard benchmarks and real-world videos.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge